Testicular Tissue Biopsy
Testicular biopsy is a medical procedure used to examine testicular tissue for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. It is a surgical procedure to remove a small tissue sample from one or both testicles. It is used to evaluate sperm production and testicular health.

What is Testicular Tissue Biopsy?

A testicular biopsy is a procedure in which a small tissue sample is removed from one or both testicles for laboratory analysis.
It is used to:
-
Diagnose the causes of male infertility, particularly when sperm production is abnormal or absent (azoospermia)
-
Retrieve sperm for in vitro fertilisation (IVF) when sperm are present in the testicles but not in the semen
-
Diagnose testicular cancer or other testicular abnormalities
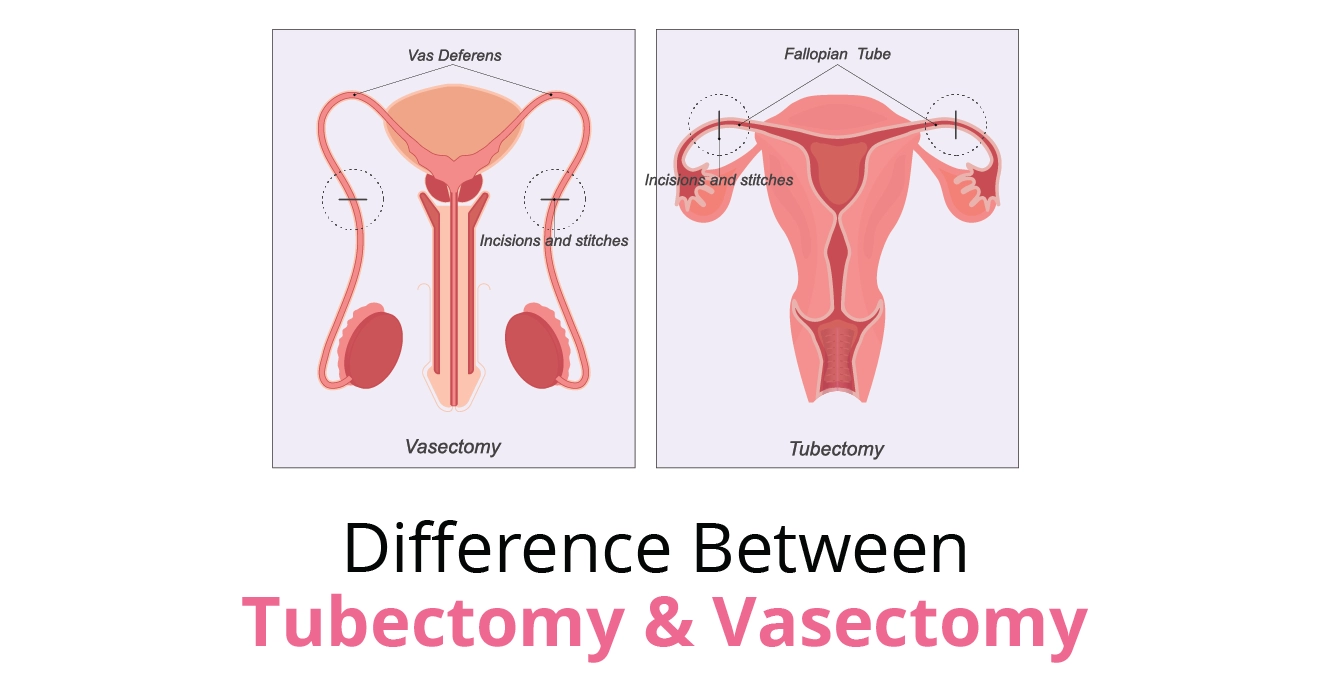
The biopsy can be performed as a percutaneous (needle) procedure or an open (surgical) procedure. In both cases, a small sample of testicular tissue is extracted for examination.
Testicular biopsy can help determine if the issue is due to a blockage or problems with sperm production within the testicles.
When is Testicular Tissue Biopsy recommended?
Testicular biopsy is often recommended when semen analysis shows a complete lack of sperm. It can help determine if the issue is due to a blockage (obstructive azoospermia) or problems with sperm production within the testicles (non-obstructive azoospermia).
Additionally, testicular biopsy is performed to retrieve sperm directly from the testicles when it is not present in the semen. The extracted sperm can then be used for IVF procedures.
Testicular biopsy may also be recommended when the cause of male infertility is unclear, and after other tests like semen analysis and hormone testing have not provided a definitive diagnosis. The biopsy can help identify underlying conditions like testicular cancer or other abnormalities that may be impacting fertility.

Testicular Tissue Biopsy: How it is done?

The biopsy can be performed in two main ways:
-
Open (Surgical) Biopsy:
-
The doctor makes a small incision in the scrotum to expose the testicle.
-
A small sample of testicular tissue is then removed using surgical instruments.
-
The incision is closed with stitches.
-
-
Percutaneous (Needle) Biopsy:
-
The doctor uses a thin needle to extract a sample of testicular tissue through the skin of the scrotum.
-
This can be done using a fine needle or a core needle biopsy, which takes a larger tissue sample.
-
No incision is made, and the needle puncture site is simply covered with a bandage.
-
Why Choose Us
Choosing the right fertility clinic is crucial for starting your family. At Birla Fertility & IVF, we offer personalised care with expert specialists guiding you every step of the way. Our advanced labs and outstanding success rates have helped over 2,30,000 patients achieve their dream of parenthood.
Frequently Asked Questions
Recent Blogs
Book an appointment
Hassle-Free Appointment Booking
Select Preferences
I know my doctor
Male Infertility Treatment in Different Cities
- Male Infertility Treatment in Jalandhar
- Male Infertility Treatment in Perinthalmanna
- Male Infertility Treatment in Thrissur
- Male Infertility Treatment in Palakkad
- Male Infertility Treatment in Kannur
- Male Infertility Treatment in Kozhikode
- Male Infertility Treatment in Ranchi
- Male Infertility Treatment in Patna
- Male Infertility Treatment in Varanasi
- Male Infertility Treatment in Gorakhpur
- Male Infertility Treatment in Meerut
- Male Infertility Treatment in Prayagraj
- Male Infertility Treatment in Kolar
- Male Infertility Treatment in Salem
- Male Infertility Treatment in Vijayapura
- Male Infertility Treatment in Nagpur
- Male Infertility Treatment in Raipur
- Male Infertility Treatment in Rewari
- Male Infertility Treatment in Jaipur
- Male Infertility Treatment in Guwahati
- Male Infertility Treatment in Siliguri
- Male Infertility Treatment in Howrah
- Male Infertility Treatment in Indore
- Male Infertility Treatment in Bhopal
- Male Infertility Treatment in Bhubaneswar
- Male Infertility Treatment in Cuttack
- Male Infertility Treatment in Surat
- Male Infertility Treatment in Ahmedabad
- Male Infertility Treatment in Mangalore
- Male Infertility Treatment in Chandigarh
- Male Infertility Treatment in Hyderabad
- Male Infertility Treatment in Lucknow
- Male Infertility Treatment in Bangalore
- Male Infertility Treatment in Chennai
- Male Infertility Treatment in Mumbai
- Male Infertility Treatment in Kolkata
- Male Infertility Treatment in Noida
- Male Infertility Treatment in Gurgaon
- Male Infertility Treatment in Delhi
Male Infertility Doctors in Different Cities
- Male Infertility Specialists in Jalandhar
- Male Infertility Specialists in India
- Male Infertility Specialists in Perinthalmanna
- Male Infertility Specialists in Thrissur
- Male Infertility Specialists in Palakkad
- Male Infertility Specialists in Kannur
- Male Infertility Specialists in Kozhikode
- Male Infertility Specialists in Ranchi
- Male Infertility Specialists in Patna
- Male Infertility Specialists in Varanasi
- Male Infertility Specialists in Gorakhpur
- Male Infertility Specialists in Meerut
- Male Infertility Specialists in Allahabad
- Male Infertility Specialists in Kolar
- Male Infertility Specialists in Salem
- Male Infertility Specialists in Vijayapura
- Male Infertility Specialists in Nagpur
- Male Infertility Specialists in Raipur
- Male Infertility Specialists in Rewari
- Male Infertility Specialists in Jaipur
- Male Infertility Specialists in Guwahati
- Male Infertility Specialists in Siliguri
- Male Infertility Specialists in Howrah
- Male Infertility Specialists in Indore
- Male Infertility Specialists in Bhopal
- Male Infertility Specialists in Bhubaneswar
- Male Infertility Specialists in Cuttack
- Male Infertility Specialists in Surat
- Male Infertility Specialists in Ahmedabad
- Male Infertility Specialists in Mangalore
- Male Infertility Specialists in Chandigarh
- Male Infertility Specialists in Hyderabad
- Male Infertility Specialists in Lucknow
- Male Infertility Specialists in Bangalore
- Male Infertility Specialists in Chennai
- Male Infertility Specialists in Mumbai
- Male Infertility Specialists in Kolkata
- Male Infertility Specialists in Noida
- Male Infertility Specialists in Gurgaon
- Male Infertility Specialists in Delhi

 Our Centers
Our Centers