Laser Assisted Hatching (LAH)
Laser-assisted hatching (LAH) is a supplementary procedure for patients undergoing in vitro fertilisation (IVF) treatment. It helps the embryo hatch from its shell and improves its chances of implanting in the uterus. Those with a history of failed IVF treatments may find this technique helpful.

What is LAH?
In its initial stages, the embryo has a hard outer covering or shell called zona pellucida. After a few days of fertilisation, the embryo hatches out of this shell to implant into the uterus. This results in a pregnancy. However, sometimes, a thicker shell makes it difficult for the embryo to break out.
With LAH, a hole is made in the shell to assist the embryo in hatching out and attaching itself to the uterine wall.
LAH is usually advised by doctors for women above 35 or those who have had failed IVF treatments in the past. It is also done on frozen embryos as freezing can harden the shell.
Fertility treatment providers offer LAH as a complementary procedure to IVF. This artificial support to the embryo improves the chances of implantation rates and a successful pregnancy.
When is LAH recommended?
LAH is typically recommended in the following scenarios:
-
Advanced maternal age: In women over 35 with infertility issues, there is a higher likelihood of the zona pellucida failing to break. This is due to the diminished quality of the egg. It further reduces the chances of the embryo implanting itself into the uterus in the IVF treatment. LAH helps break the shell and assists the embryo in attaching to the uterine walls.
-
Diminished Ovarian Reserve: This can occur due to injury, disease or as a result of ageing. 10% to 30% of patients with infertility have a diminished ovarian reserve (DOR). IVF and LAH are recommended for women with DOR to increase their chances of pregnancy.
-
Repeated IVF Failures: Failed IVF is when good-quality embryos fail to implant or when a pregnancy ends in a miscarriage. IVF failures happen due to chromosomal abnormalities, poor quality of the egg and embryo, uterine abnormalities, high maternal age, sperm quality and the couple’s health condition.

What are the steps of LAH?
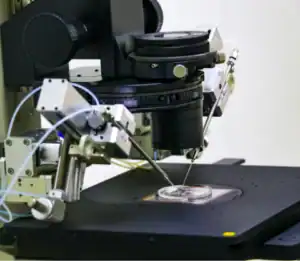
The LAH procedure consists of the following steps:
1. Stimulation: First, hormonal stimulation is employed to help produce multiple eggs. These eggs are observed and then retrieved once they reach their ideal size. This step is important as it ensures the availability of enough healthy eggs for the IVF treatment.
2. Fertilisation: These eggs are then exposed to high-quality sperm in a laboratory. This is where fertilisation occurs. These fertilised eggs, also called embryos, are then closely monitored while they grow.
3. Development of the Embryo: An embryologist monitors the development and progress of the embryo until it reaches the blastocyst stage. A blastocyst is made up of two parts: the inner group of cells and the trophectoderm, or the outer group of cells that prompts the uterine contact.
4. Laser Assisted Hatching: This is the stage where a laser is employed to make a crack or a hole in the shell of the embryo. A strong infra-red laser is focused on the zona pellucida under a microscope. It is a quick process of a few seconds that helps the embryo hatch out of the shell.
5. Transferring of the Embryo: Once the embryo hatches out of its shell, it is placed into the mother’s uterus. A thin catheter is used to transfer the embryo with the hope that it implants and initiates a pregnancy.
Why Choose Us
Choosing the right fertility clinic is crucial for starting your family. At Birla Fertility & IVF, we offer personalised care with expert specialists guiding you every step of the way. Our advanced labs and outstanding success rates have helped over 2,30,000 patients achieve their dream of parenthood.
Things to Remember for Laser Assisted Hatching
Before the Treatment
- The LAH procedure is carried out in a laboratory by an embryologist. The embryo is transferred from the culture dish to the dish reserved for the LAH process. The dish is then placed onto a micromanipulation microscope for the laser treatment. The hatched embryo will be delivered into your uterus after the procedure is complete.
During the Treatment
- LAH is carried out three days after the embryo has developed.
- A special laser is used for the procedure that is conducted in a laboratory.
- The laser is focused on the shell of the embryo to make a hole in it.
- It is a safe procedure and the laser does not reach the embryo which ensures its safety.
- The procedure is carried out with extreme care and accuracy and is preferred over chemical or manual methods.
After the Treatment
- While the procedure does not cause any pain, your doctor may give you a mild sedative to help you relax.
- A thin catheter will be placed into your uterus through the vagina.
- A syringe containing the embryo in a fluid will be attached to the other end of the catheter.
- Through the syringe and the catheter, the embryo will be gently placed into your uterus.
- The embryo will attach itself to your uterine lining in about 6 to 10 days.
Frequently Asked Questions
Recent Blogs
Book an appointment
Hassle-Free Appointment Booking
Select Preferences
I know my doctor
IVF Cost in Different Cities
- IVF Cost in Jalandhar
- IVF Cost in India
- IVF Cost in Siliguri
- IVF Cost in Perinthalmanna
- IVF Cost in Patna
- IVF Cost in Chennai
- IVF Cost in Vijayapura
- IVF Cost in Mumbai
- IVF Cost in Kolar
- IVF Cost in Bangalore
- IVF Cost in Thrissur
- IVF Cost in Salem
- IVF Cost in Palakkad
- IVF Cost in Mangalore
- IVF Cost in Kannur
- IVF Cost in Kozhikode
- IVF Cost in Bhopal
- IVF Cost in Indore
- IVF Cost in Hyderabad
- IVF Cost in Nagpur
- IVF Cost in Jaipur
- IVF Cost in Raipur
- IVF Cost in Guwahati
- IVF Cost in Chandigarh
- IVF Cost in Ranchi
- IVF Cost in Ahmedabad
- IVF Cost in Surat
- IVF Cost in Cuttack
- IVF Cost in Bhubaneswar
- IVF Cost in Howrah
- IVF Cost in Kolkata
- IVF Cost in Meerut
- IVF Cost in Allahabad
- IVF Cost in Noida
- IVF Cost in Gorakhpur
- IVF Cost in Varanasi
- IVF Cost in Lucknow
- IVF Cost in Rewari
- IVF Cost in Gurgaon
- IVF Cost in Delhi
IVF Treatment in Different Cities
- IVF Treatment in Jalandhar
- IVF Treatment in Siliguri
- IVF Treatment in Perinthalmanna
- IVF Treatment in Patna
- IVF Treatment in Chennai
- IVF Treatment in Vijayapura
- IVF Treatment in Delhi
- IVF Treatment in Kolar
- IVF Treatment in Thrissur
- IVF Treatment in Salem
- IVF Treatment in Palakkad
- IVF Treatment in Mangalore
- IVF Treatment in Kannur
- IVF Treatment in Kozhikode
- IVF Treatment in Bhopal
- IVF Treatment in Indore
- IVF Treatment in Hyderabad
- IVF Treatment in Nagpur
- IVF Treatment in Jaipur
- IVF Treatment in Raipur
- IVF Treatment in Guwahati
- IVF Treatment in Chandigarh
- IVF Treatment in Ranchi
- IVF Treatment in Ahmedabad
- IVF Treatment in Surat
- IVF Treatment in Cuttack
- IVF Treatment in Bhubaneswar
- IVF Treatment in Howrah
- IVF Treatment in Kolkata
- IVF Treatment in Meerut
- IVF Treatment in Prayagraj
- IVF Treatment in Noida
- IVF Treatment in Gorakhpur
- IVF Treatment in Varanasi
- IVF Treatment in Lucknow
- IVF Treatment in Rewari
- IVF Treatment in Gurgaon
- IVF Treatment in Bangalore
- IVF Treatment in Delhi
IVF Doctors in Different Cities
- IVF Doctors in Jalandhar
- IVF Doctors in Prayagraj
- IVF Doctors in India
- IVF Doctors in Perinthalmanna
- IVF Doctors in Thrissur
- IVF Doctors in Palakkad
- IVF Doctors in Kannur
- IVF Doctors in Kozhikode
- IVF Doctors in Ranchi
- IVF Doctors in Patna
- IVF Doctors in Varanasi
- IVF Doctors in Gorakhpur
- IVF Doctors in Meerut
- IVF Doctors in Allahabad
- IVF Doctors in Kolar
- IVF Doctors in Salem
- IVF Doctors in Vijayapura
- IVF Doctors in Nagpur
- IVF Doctors in Raipur
- IVF Doctors in Jaipur
- IVF Doctors in Guwahati
- IVF Doctors in Siliguri
- IVF Doctors in Howrah
- IVF Doctors in Indore
- IVF Doctors in Bhopal
- IVF Doctors in Bhubaneswar
- IVF Doctors in Cuttack
- IVF Doctors in Surat
- IVF Doctors in Ahmedabad
- IVF Doctors in Mangalore
- IVF Doctors in Chandigarh
- IVF Doctors in Hyderabad
- IVF Doctors in Lucknow
- IVF Doctors in Bangalore
- IVF Doctors in Chennai
- IVF Doctors in Mumbai
- IVF Doctors in Kolkata
- IVF Doctors in Noida
- IVF Doctors in Gurgaon
- IVF Doctors in Delhi

 Our Centers
Our Centers