Table of Contents
Want to start a family but have infertility issues coming your way? Thanks to modern medical advancements, your dream of becoming a parent is not as far as you may think. Among the different choices to achieve parenthood, the two most common that you must have heard are IVF and surrogacy. But how will you choose which one is right for you? How are these different? In this blog, let’s uncover the difference between IVF and surrogacy, know about their costs, success rates, and all those factors that will help you make an informed decision.
What is IVF?
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a fertility treatment where an egg and sperm are fertilised outside the woman’s body in a controlled environment of a lab. The resulting embryo is then transferred to the woman’s uterus for implantation. IVF is a great option for both female and male infertility.
IVF Process
The IVF journey has to pass several stages:
- Ovarian Stimulation – Fertility medications are given to stimulate egg production.
- Egg Retrieval – Mature eggs are collected from the ovaries.
- Sperm Collection & Preparation – A sperm sample is obtained from the male partner or a sperm donor using techniques like sperm wash.
- Fertilisation – The egg and sperm are combined in a lab.
- Embryo Transfer – A healthy embryo is transferred into the uterus.
- Pregnancy Test – After two weeks, a pregnancy test is done to confirm pregnancy.
Why Choose IVF?
IVF has helped millions of couples across the world achieve parenthood. The IVF treatment:
- Helps those facing infertility due to blocked fallopian tubes or unexplained infertility
- Provides a chance for pregnancy even in cases of low sperm count
- Allows genetic connection to the baby
- Can be performed with donor sperm or donor eggs
Success Rate of IVF Treatment
The IVF success rate depends on various factors, including age, overall health, and embryo quality.
| Age Group | IVF Success Rate |
| Under 35 | 50-55% |
| 35-37 | 40-45% |
| 38-40 | 25-30% |
| Above 40 | 10-20% |
As seen above, success rates decline with age, making it essential to consider IVF at the right time.
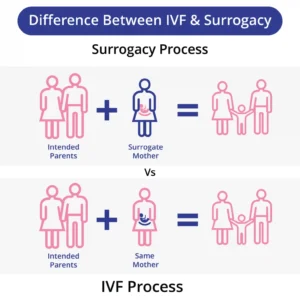
What is Surrogacy?
Surrogacy is a fertility treatment where another woman (the surrogate) carries and delivers a baby for the intended parents. This is often chosen by individuals who cannot carry a pregnancy due to medical reasons.
Types of Surrogacy
Surrogacy can be classified into two main types:
1. Traditional Surrogacy
In traditional surrogacy, the surrogate is biologically related to the child. This means her own egg is fertilised using sperm from the intended father or a donor, typically through intrauterine insemination (IUI) or in vitro fertilisation (IVF).
2. Gestational Surrogacy
In gestational surrogacy, the surrogate carries a baby that is not genetically related to her. An embryo is created using the intended parents’ (or donors’) sperm and egg through IVF and then transferred into the surrogate’s uterus.
Success Rate of Surrogacy
The surrogacy success rate is generally higher than IVF alone because healthy surrogates are chosen specifically for the process.
| Type | Success Rate |
| Gestational Surrogacy | 75-80% |
| Traditional Surrogacy | 55-60% |
IVF vs Surrogacy: Which is the Better Option?
Here’s a quick comparison of IVF and surrogacy based on key factors:
| Factor | IVF | Surrogacy |
| Legal Aspects | Fewer legal formalities | Involves legal contracts and regulations |
| Cost | ₹1.5 – 2.5 lakhs per cycle | ₹10 – 20 lakhs (higher cost due to surrogate compensation) |
| Medical Procedure | Involves ovarian stimulation and embryo transfer | Involves IVF and pregnancy through a surrogate |
| Personal Choice | Suitable for those who want to carry their child | Ideal for those unable to carry a pregnancy |
| Genetic Connection | Parents are biologically related to the baby | Baby is genetically related to intended parents in gestational surrogacy |
Common Myths and Facts About IVF & Surrogacy
Myth 1: IVF always results in twins or triplets
Fact: While IVF increases the chance of multiple births, single embryo transfer reduces this risk.
Myth 2: Surrogates can claim legal rights over the baby
Fact: In gestational surrogacy, the baby is biologically related to the intended parents and legal agreements prevent disputes.
Myth 3: IVF is only for women over 35
Fact: IVF is an option for any couple or individual facing fertility issues, regardless of age.
Myth 4: Surrogacy is only for the wealthy
Fact: While surrogacy is costlier than IVF, financing options and payment plans are available.
Factors to Consider for Decision-Making between IVF and Surrogacy
- Medical Considerations: Couples facing fertility challenges often opt for IVF when biological parenthood is a primary goal. Surrogacy is chosen when carrying a pregnancy is not feasible due to medical reasons.
- Personal Preferences: Personal preferences play a significant role. Some may prioritise a genetic connection and choose IVF, while others may opt for surrogacy to overcome specific medical challenges or achieve parenthood without carrying the pregnancy.
Choosing What’s Best for You!
Deciding between IVF and surrogacy is deeply personal. It is not just about medical procedures or costs—it’s about your journey, your emotions, and your dreams of parenthood. If you are longing to experience pregnancy firsthand, IVF might be the right path. If carrying a baby is not an option, but you are eager to hold your little one in your arms, surrogacy could be the answer. Every journey is unique and you are not alone in this. Millions have walked this path before, and with the right support, you can too. Take a deep breath, trust the process, and know that your dream of parenthood is possible. Still unsure? Let’s talk. Our experts at Birla Fertility & IVF are here to guide you every step of the way.
Our Fertility Specialists
Related Blogs
To know more
Birla Fertility & IVF aims at transforming the future of fertility globally, through outstanding clinical outcomes, research, innovation and compassionate care.
Had an IVF Failure?
Talk to our fertility experts

 Our Centers
Our Centers