What Should You Eat Post Embryo Transfer

Table of Contents
- What Happens After the Embryo Transfer Phase?
- How Diet Can Increase the Chances of Successful Implantation
- Diet Before Embryo Transfer
- Importance of Diet Chart After Embryo Transfer
- After Embryo Transfer Diet Chart
- Significance of Key Nutrients for Post Embryo Transfer Diet
- Foods to Avoid After Embryo Transfer
- Role of Hydration in Embryo Transfer
- How Lifestyle Impacts Embryo Transfer
- Conclusion
Opting for an IVF treatment is one of the life-altering decisions a woman takes in her lifetime. Which is why it can take an emotional toll on some women, after all it is a significant step towards achieving her dream of motherhood. During this phase, she needs all the support she can get, both mentally and physically.
After embryo transfer, the diet chart plays a vital role in enhancing the chances of a successful pregnancy. In this blog, we will explore the best foods to eat after embryo transfer, and types of food to avoid after embryo transfer in order to ensure the best outcome. Additionally, you will find a comprehensive diet chart that you can follow after embryo transfer, and a few tips on looking after yourself during this delicate phase.
What Happens After the Embryo Transfer Phase?
After embryo transfer, the next crucial step is implantation. This usually happens 7-10 days after the embryo transfer. Here’s what happens:
- The embryo attaches itself to the lining of your uterus. Eating right and drinking enough water can help this process.
- Your body starts making a hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). This hormone supports early pregnancy.
- The lining of your uterus gets thicker and ready for embryo implantation.
- You might start experiencing some positive signs after embryo transfer, including mild cramps, spotting, or mood swings. This indicates successful pregnancy.
Eating a balanced diet and living a healthy lifestyle during this time is vital for all these things to happen smoothly.
How Diet Can Increase the Chances of Successful Implantation
Following after embryo transfer diet chart and a healthy lifestyle can result in increasing the chances of successful implantation. Eating a nutrient-rich diet can:
- Support Hormonal Balance: Proper nutrition helps maintain balanced hormone levels and is definitely essential for a conducive uterine environment.
- Improve Immune Function: A strong immune system can better support implantation and early pregnancy.
- Promote Healthy Blood Flow: Iron and omega-3 fatty acids boost blood flow to the uterus, which also promotes the embryo to develop further.
- Reduce Inflammation: Anti-inflammatory foods like berries, nuts, and fatty fish help reduce inflammation, which can negatively interfere with implantation.
Diet Before Embryo Transfer
Eating healthy is important not just after the embryo transfer process but also in the days leading up to it. Keep these tips in mind:
- Opt for fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated.
- Stay away from processed, canned, and junk foods.
- Include healthy fats from nuts, seeds, and avocados.
- Make sure you’re getting enough folic acid. This supplement is essential for your baby’s development.
Eating healthy is important not just after the embryo transfer process but also in the days leading up to it. Keep these tips in mind:
Importance of Diet Chart After Embryo Transfer
A well-balanced diet is high in essential nutrients, which promotes the body’s natural processes, including embryo implantation. If you think that the last step of the IVF process, i.e. embryo transfer, is the end of the treatment, then the answer to that is NO! It’s important to remember that there are still crucial steps, lifestyle choices, and certain food items which need to be included in after embryo transfer diet chart. Such changes can significantly impact your chances of a successful outcome.
A good diet after embryo transfer can help maintain appropriate hormone levels, increase energy, and strengthen the immune system, all of which can increase the chances of successful implantation. Here is an after-embryo transfer diet chart with alternative options, allowing you to choose according to your preferences.
After Embryo Transfer Diet Chart
You can follow this after embryo transfer diet chart, however, it is always better to connect with a nutritionist to get your custom-made diet according to your age and body mass index (BMI).
| Meal | Option 1 | Option 2 | Option 3 |
| Breakfast | Oats porridge with chia seeds, topped with fresh berries and honey | Moong dal cheela with Greek yogurt | Whole wheat toast with avocado spread and a boiled egg |
| Lunch | Brown rice with palak paneer (spinach and cottage cheese curry) and cucumber raita | Quinoa salad with mixed vegetables, chickpeas, and lemon-tahini dressing | Chicken curry with whole wheat roti and steamed broccoli |
| Dinner | Grilled fish with sweet potato mash and sautéed greens | Dal makhani (creamy lentils) with brown rice and mixed greens salad | Stir-fried tofu with bell peppers and quinoa |
Alternatives for Vegetarian
- Replace chicken or fish with tofu, tempeh, or paneer.
- Use legumes like chickpeas, black beans, and lentils as protein sources.
Alternatives For Non-Vegetarian
- Include lean meats like chicken and turkey.
- Opt for fatty fish like salmon and mackerel for omega-3s.
- Carefully steer clear of any kind of food related allergies.>
Significance of Key Nutrients for Post Embryo Transfer Diet
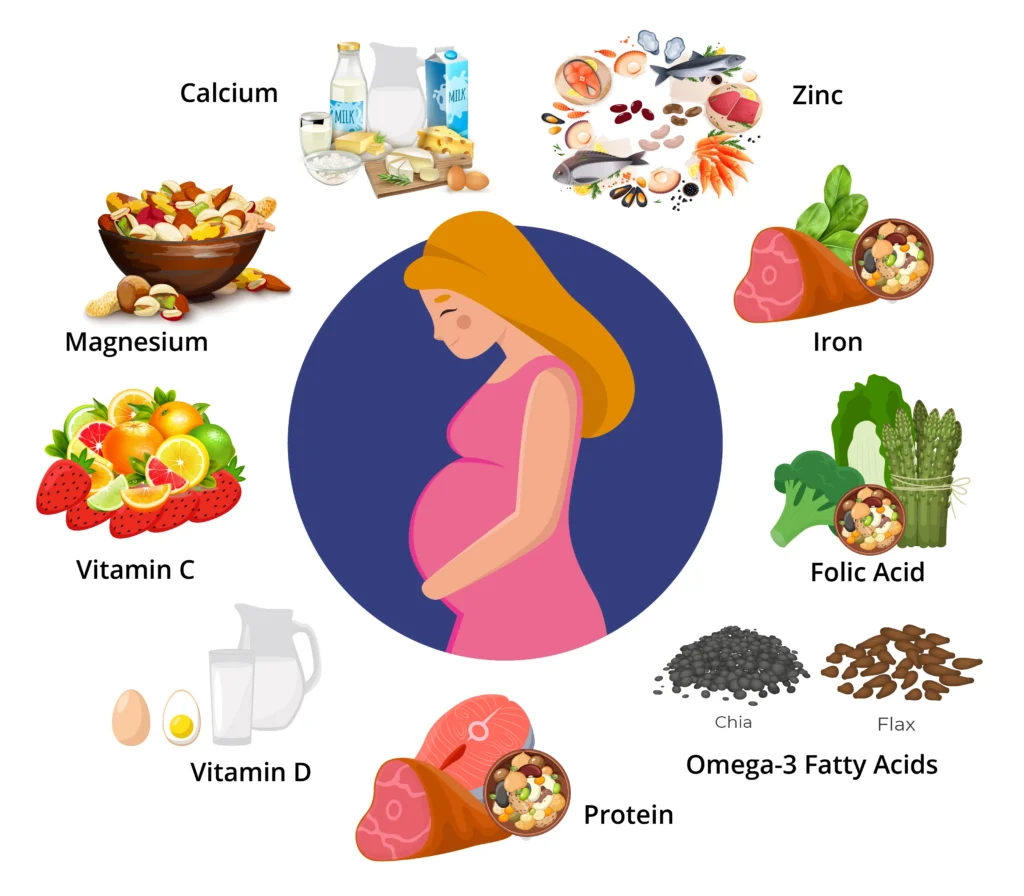

Fertility experts recommend including certain nutrients in after embryo diet chart to increase the chances of successful implantation, some of them are:
- Folic Acid:It is essential for DNA synthesis, and cell division. Also, it reduces the risk of neural tube defects. Leafy greens (spinach, kale), lentils, asparagus,and fortified cereals are some food items that are enriched in folic acid.
- Vitamin D: It supports immune function and bone health and aids in calcium absorption. Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), fortified dairy products, and egg yolks are a few food items consisting of vitamin D.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: This helps in reducing inflammation, support fetal brain development, and improves cardiovascular health. You can include fatty fish (salmon, sardines),flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts in your diet for omega-3 fatty acids.
- Iron: This is crucial for oxygen transport in the blood, supports energy levels, and prevents anaemia. Adding red meat, spinach, lentils, and quinoa can fulfill the iron requirement in the body.
- Calcium: This is essential for bone health and the development of the fetal skeletal system. Dairy products (milk, cheese, yogurt), almonds, and tofu are some reliable sources of calcium.
- Vitamin C: You must include citrus fruits (oranges, lemons), strawberries, bell peppers, and broccoli in your diet. These are enriched in vitamins and act as antioxidants, which enhance iron absorption and support the body’s immune system.
- Protein: It is highly necessary in the body and helps in tissue repair, muscle growth, and overall cell function. Lean meats (chicken, turkey), beans, lentils, and dairy products are good sources of protein and aid in embryo implantation.
- Magnesium: Magnesium is necessary to regulate muscle and nerve function, blood sugar levels, and blood pressure. It is important to know tha nuts (almonds, cashews), whole grains, and dark chocolate are good sources of magnesium.
- Zinc: Zinc is very important for females after embryo transfer as it supports immune function, cell division, and fetal development. Though meat, shellfish, legumes, and seeds contain zinc, in some cases, experts advise considering zinc supplements.
- Fiber: Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes are high in fiber. They are much-needed to include in the diet to promote healthy digestion and prevent constipation.
Foods to Avoid After Embryo Transfer
There are certain foods to avoid after embryo transfer which can impact embryo implantation negatively:
- Avoid fish like swordfish and king mackerel, which contain high levels of mercury and can harm fetal development.
- Avoid unpasteurized milk, cheese, and other dairy products to avoid the risk of bacterial infections like listeriosis.
- Limit or avoid intake of processed and junk foods, which are high in unhealthy fats, sugars, and preservatives that can negatively affect overall health and fertility.
- Reduce or avoid caffeine consumption from coffee, tea, and energy drinks, as high caffeine intake can negatively impact embryo transfer outcomes.
- Avoid all alcoholic beverages, as they can interfere with implantation and fetal development, increasing the risk of miscarriage and other complications.
Role of Hydration in Embryo Transfer
Staying hydrated is crucial both before and after the embryo transfer process. Here’s why fluids are important in this phase:
- Before the procedure, drinking enough water helps fill up your bladder. This is needed for ultrasound-guided embryo transfer.
- Water helps your body absorb the medications you take before the IVF procedure.
- Staying hydrated keeps your hormones in balance, which is key for implantation.
- Water boosts your immune system and lowers the risk of infections.
- It helps flush out toxins from your blood and improves blood flow.
Fluids to Consume
- Water: It is the main source of hydration. Aim for at least 6-8 glasses a day.
- Herbal teas: Some herbal teas, like peppermint or chamomile, can be soothing and keep you hydrated.
- Low-sugar juices: Fresh juices without added sugars can be good for you.
Fluids to Avoid
- Alcohol: Say no to alcohol. It can negatively affect hormonal balance and overall health.
- Caffeinated drinks: Go easy on the caffeine. It can dehydrate you and affect your hormone levels.
- Unpasteurised juices: They have low nutritional value and carry the risk of bacterial contamination.
How Lifestyle Impacts Embryo Transfer
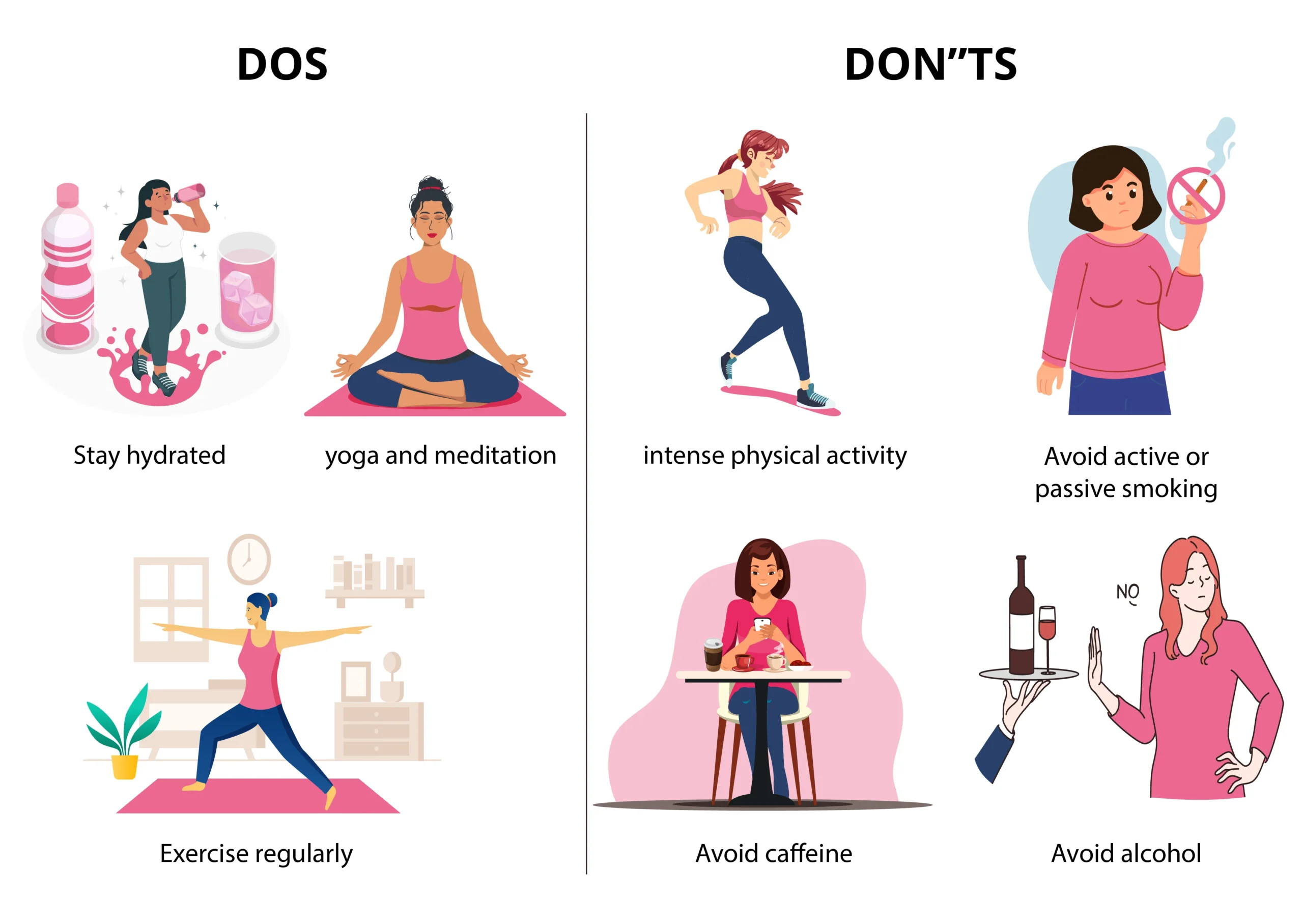
Why Lifestyle Matters!
Smoking and drinking can lower your chances of successful implantation. If you smoke, your implantation odds can drop by 50% compared to non-smokers.
Being overweight can affect how your body processes hormones, your menstrual cycles, and your ability to carry a pregnancy to term.
High stress levels can negatively impact fertility and reduce the chances of a successful first-time IVF.
What To Do
- Maintain a balanced diet: Focus on whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. A balanced diet gives you the necessary nutrients for implantation and early pregnancy.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to maintain optimal hydration levels. Aim for an uncomfortably full bladder before the procedure to help with visualisation during the ultrasound.
- Exercise regularly: Moderate physical activity can help you maintain a healthy weight and reduce stress. However, avoid intense workouts that may disrupt the implantation process.
- Manage stress: Take part in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or counselling. Lower stress levels can improve your overall fertility and well-being.
What to Avoid
- Smoking and alcohol: Quit smoking and drinking alcohol at least three months before starting IVF. These habits greatly reduce the chances of successful implantation.
- Too much caffeine: Limit caffeine intake as it can act as a diuretic and reduce hydration levels, potentially affecting embryo transfer.
- High-stress activities: Avoid activities that cause a lot of stress; high stress levels can negatively impact fertility and implantation.
- Unhealthy foods: Implantation foods to avoid include processed foods, trans fats, excessive caffeine, and alcohol. Choose nutrient-dense foods that support your overall health and fertility.
Conclusion
A balanced diet after embryo transfer can considerably increase the odds of successful implantation and a healthy pregnancy. You may help your body during this critical phase by eating nutrient-rich meals, sticking to a planned diet chart, and adopting conscious lifestyle choices. Also, for better guidance always speak with your fertility expert for advice and suggestions before starting any random routine to avoid any complications.
Our Fertility Specialists
Related Blogs
To know more
Birla Fertility & IVF aims at transforming the future of fertility globally, through outstanding clinical outcomes, research, innovation and compassionate care.
Had an IVF Failure?
Talk to our fertility experts

 Our Centers
Our Centers