NT/NB Scan: Why It’s Essential for a Healthy Pregnancy?

Table of Contents
- What is the Purpose of the NT/NB Scan?
- Why is the NT/NB Scan Beneficial for Your Pregnancy?
- What is the NT/NB Scan Procedure?
- When is the Best Time for an NT/NB Scan?
- How is the NT/NB Scan Performed?
- Who Performs the NT/NB Scan?
- How long does it take to get the results of an NT/NB Scan?
- Are there any Risks Associated with the NT/NB Scan?
- Preparing for the NT/NB Scan:
- Normal Range and Timing of the NT/NB Scan
- Do Abnormal Results Mean the Baby has a Syndrome?
- What Factors Can Affect the NT/NB Scan Results?
- What should I do if the NT/NB Scan Results are Abnormal?
- Alternatives to the NT/NB Scan
- Cost of the NT/NB Scan in India:
- FAQs
- NT/NB scan is done in which week of pregnancy?
- What is the normal range of the NT/NB scan test?
- Does an NT/ NB scan show gender?
- What is the cost of an NT NB scan in India?
- What is the size of the NB at 12 weeks?
- Is fasting required for an NT-NB scan?
- What is the best time for an NT-NB scan?
- How accurate is the NT/NB scan?
As an expectant parent, you may encounter a variety of medical jargon and procedures, which can initially seem daunting.
The NT/NB scan, also known as a nuchal translucency scan, is one such crucial examination. This specialist ultrasound test is essential for evaluating the health and development of your unborn child and is usually done between weeks 11 and 14 of pregnancy.
We’ll cover the specifics of the NT/NB scan in this post, including its purpose, method, and significance during your pregnancy journey.
What is the Purpose of the NT/NB Scan?
According to reports, it is observed that when NT/NB is combined with other blood tests, it enables early detection of potential chromosomal abnormalities in your developing foetus, particularly Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, and Patau syndrome, with an accuracy rate of 70-85%.
This helps with making informed decisions. The key focus of this test is:
- Nuchal Translucency– The test helps measure the fluid present at the back of your baby’s neck. This helps with identifying a higher risk of chromosomal abnormalities.
- Nasal Bone Development– The presence or absence of a nasal bone is assessed during the scan. A well-developed nasal bone may indicate a lower risk of chromosomal abnormalities.
Did You Know?
The NT/NB scan, performed between the 11th and 14th weeks of pregnancy, is a crucial prenatal screening test that assesses the risk of chromosomal abnormalities like Down syndrome. This non-invasive ultrasound examination measures the thickness of the nuchal translucency and evaluates the presence of the nasal bone, providing valuable insights into the baby’s health.
Why is the NT/NB Scan Beneficial for Your Pregnancy?
The NT/NB scan plays a vital role in your prenatal care for several reasons:
- Early detection of chromosomal abnormalities: It provides an early indication of the risk of chromosomal abnormalities, allowing you to make informed decisions about further testing and potential interventions.
- Identification of structural problems: The scan can identify structural issues such as spina bifida, skeletal defects, and heart malformations.
- More precise delivery date estimation: It helps in estimating a more accurate due date for your baby’s arrival.
- Assessment of pregnancy failure risk: Early detection of any concerns for pregnancy failure.
- Identification of multiple foetuses: It can determine if you are carrying more than one baby.
What is the NT/NB Scan Procedure?
The NT/NB scan is a non-invasive ultrasound examination that can be performed in two ways, depending on the clarity of the images and your baby’s position:
- Abdominal Ultrasound: The technician uses a transducer on your abdomen to capture images and measurements of your baby. This method is generally preferred but may require a full bladder to obtain clear images.
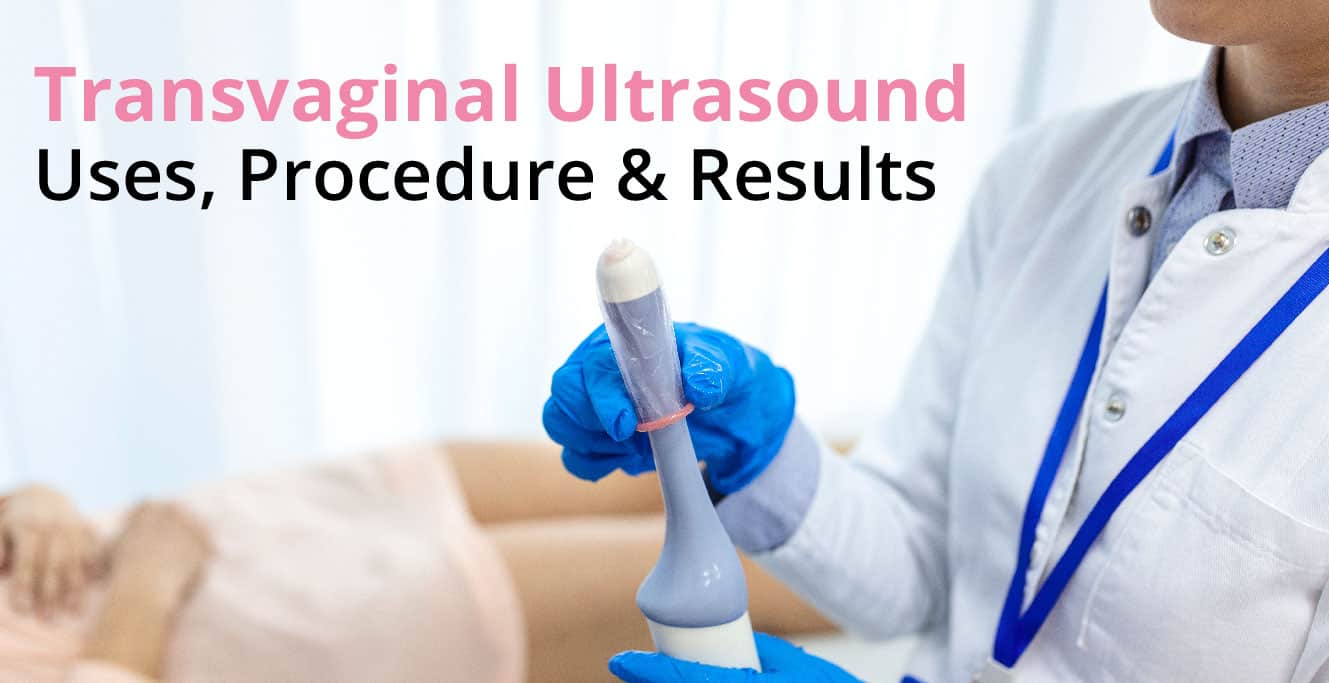
- Transvaginal Ultrasound: A well-lubricated ultrasound probe is inserted into your vagina to scan your uterus. This method is used when the abdominal ultrasound is not clear or when your baby is in a position that makes abdominal scanning difficult.
The procedure typically takes between 20 to 30 minutes and is painless, although the transvaginal method may cause some discomfort.
When is the Best Time for an NT/NB Scan?
It’s important to note that the NT/NB scan is usually performed between the 11th and 14th weeks of pregnancy. Most doctors recommend getting it done around the 12th week which is considered the ideal NT/NB scan time.
This timeframe is critical because the clear space at the back of your baby’s neck begins to close up after 15 weeks, making it essential to conduct the scan before this period.
How is the NT/NB Scan Performed?
The procedure typically takes between 20 to 30 minutes and is painless, although the transvaginal method may cause some discomfort. Here’s what you can expect:
- You’ll lie down on an examination table.
- A trained sonographer will apply a special gel on your belly.
- The sonographer will use a transducer to capture images of your baby.
- They’ll measure the fluid-filled space at the back of your baby’s neck (called the nuchal translucency).
- They’ll also check other markers like your baby’s nasal bone and heart function.
Who Performs the NT/NB Scan?
A trained sonographer typically performs the NT and NB scans. They work under the supervision of an obstetrician or a foetal medicine specialist.
The sonographer’s expertise can significantly impact the accuracy of the scan. Some sonographers have worked with pioneers in the field, which can significantly enhance their skills and expertise.
How long does it take to get the results of an NT/NB Scan?
NT (Nuchal Translucency) Scan:
- Usually performed between 11–14 weeks of pregnancy.
- Preliminary results are often available immediately after the scan.
- A detailed risk assessment for chromosomal conditions may take 1–3 days, depending on the laboratory.
NB (Nasal Bone) Scan:
- Often performed in conjunction with the NT scan.
- Results for the presence and measurement of the nasal bone are usually available immediately.
Are there any Risks Associated with the NT/NB Scan?
The good news is that the NT/NB scan in pregnancy itself is non-invasive and risk-free. You don’t have to worry about any harm to you or your baby.
However, if the scan shows abnormal results, your doctor may recommend further diagnostic tests, such as chorionic villus sampling (CVS) or amniocentesis. These tests carry a small risk of pregnancy loss.
Preparing for the NT/NB Scan:
To ensure the best possible results from your NT/NB scan, there are a few things you can do to prepare:
- Schedule a blood test: It is recommended to have blood drawn 48 hours prior to the scan. The results will be combined with the ultrasound measurements for a more accurate risk assessment.
- Maintain a full bladder: If you’re having an abdominal ultrasound, a full bladder may be required to obtain clear images. Your doctor will guide you on how much water to drink and when to drink it before the scan.
By following these simple steps, you can help your doctor obtain the most accurate measurements and assessment during your NT/NB scan.
Normal Range and Timing of the NT/NB Scan
The normal range for the nuchal translucency measurement is typically less than 3.5 mm. Here are some general guidelines:
| Measurement Range | Interpretation |
| Less than 3.5 mm | Normal range |
| 3.5 mm to 6 mm | Borderline |
| 6 mm or higher | Elevated risk |
Do Abnormal Results Mean the Baby has a Syndrome?
No, abnormal screening results do not confirm a syndrome. NT–NB scans are screening tests, not diagnostic tests. An abnormal result only means a higher risk, not a definite condition. Many babies with abnormal screening results are born completely healthy. Further tests (like NIPT, CVS, or amniocentesis) may be advised for confirmation.
What Factors Can Affect the NT/NB Scan Results?
Several things can influence the results of your USG NT/NB scan:
- Your baby’s position: If your baby is in an awkward position, it may be hard to get clear images.
- The sonographer’s skill: The sonographer’s expertise can affect how accurately they take measurements.
- Additional markers: The presence or absence of specific markers, such as the nasal bone, tricuspid valve flow, and ductus venosus resistance, can influence the risk assessment.
What should I do if the NT/NB Scan Results are Abnormal?
If your NT/NB scan shows increased nuchal translucency or other abnormal markers, don’t panic. Your doctor will likely recommend additional tests to confirm or rule out any chromosomal abnormalities.
These tests may include:
- Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT)
- Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)
- Amniocentesis
Let’s learn more about these tests in the next section.
It’s important to note that the NT/NB scan is usually performed between the 11th and 14th weeks of pregnancy. This timeframe is critical because the clear space at the back of your baby’s neck begins to close up after 15 weeks, making it essential to conduct the scan before this period.
Alternatives to the NT/NB Scan
While the NT/NB scan is a highly effective screening tool, there are alternatives available for women who prefer or require additional testing:
- Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT): Also known as cell-free DNA testing (cfDNA), this test analyzes the DNA present in the mother’s blood to detect chromosomal abnormalities. NIPT is a highly accurate screening method that can be performed as early as 10 weeks into the pregnancy.
- Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS): This diagnostic test involves removing a small sample of the placenta for genetic testing. CVS is typically performed between 10 and 13 weeks of pregnancy and can provide definitive information about chromosomal abnormalities.
- Amniocentesis: Another diagnostic test, amniocentesis, involves removing a small amount of amniotic fluid for genetic testing. This test is usually performed between 15 and 20 weeks of pregnancy and can provide conclusive results about chromosomal abnormalities.
Your doctor can help you determine which tests are most appropriate for your individual situation and provide guidance on the benefits and risks associated with each option.
Cost of the NT/NB Scan in India:
The cost of an NT/NB scan can vary depending on your location, hospital, and doctor. In India, the cost typically ranges from ₹1,500 to ₹5,000, although this can vary widely. It’s best to consult with your doctor or insurance company to understand the specific costs associated with your case. Connect with our expert team at Birla Fertility & IVF to know more.
FAQs
NT/NB scan is done in which week of pregnancy?
The NT/NB scan is generally done between the 11th and 14th week of pregnancy.
What is the normal range of the NT/NB scan test?
The normal range of the NT/NB scan test is less than 3.5 mm.
Does an NT/ NB scan show gender?
No, an NT/NB scan does not reveal the baby’s gender.
What is the cost of an NT NB scan in India?
The cost of an NT/NB scan in India is between ₹1,500 to ₹5,000.
What is the size of the NB at 12 weeks?
The nasal bone (NB) is usually about 2.5–3.5 mm in length at 12 weeks of pregnancy.
Is fasting required for an NT-NB scan?
No, fasting is not required during an NT/NB scan. You can eat and drink normally before the scan is performed.
What is the best time for an NT-NB scan?
The best time for an NT–NB scan is between 11 weeks and 13 weeks 6 days of pregnancy, when measurements are most accurate.
How accurate is the NT/NB scan?
An NT/NB scan is generally accurate, especially when performed between the 11th and 13th weeks of pregnancy.
Our Fertility Specialists
Related Blogs
To know more
Birla Fertility & IVF aims at transforming the future of fertility globally, through outstanding clinical outcomes, research, innovation and compassionate care.
Had an IVF Failure?
Talk to our fertility experts

 Our Centers
Our Centers