Endometriosis vs PCOS: What is the Difference

Table of Contents
Have you ever wondered how two seemingly similar reproductive disorders could be so different? Endometriosis and PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome) are often mistaken for one another due to their overlapping symptoms.
According to the Times of India –10% of teenagers and 30% of women in their 20s suffer from PCOS in India. Endometriosis affects 10% of women worldwide in the reproductive age range. Both are divergently different situations, although they can occur simultaneously in the same individual.
In this article, let’s understand the difference between PCOS and endometriosis, which is crucial for effective diagnosis and management.
What is Endometriosis?
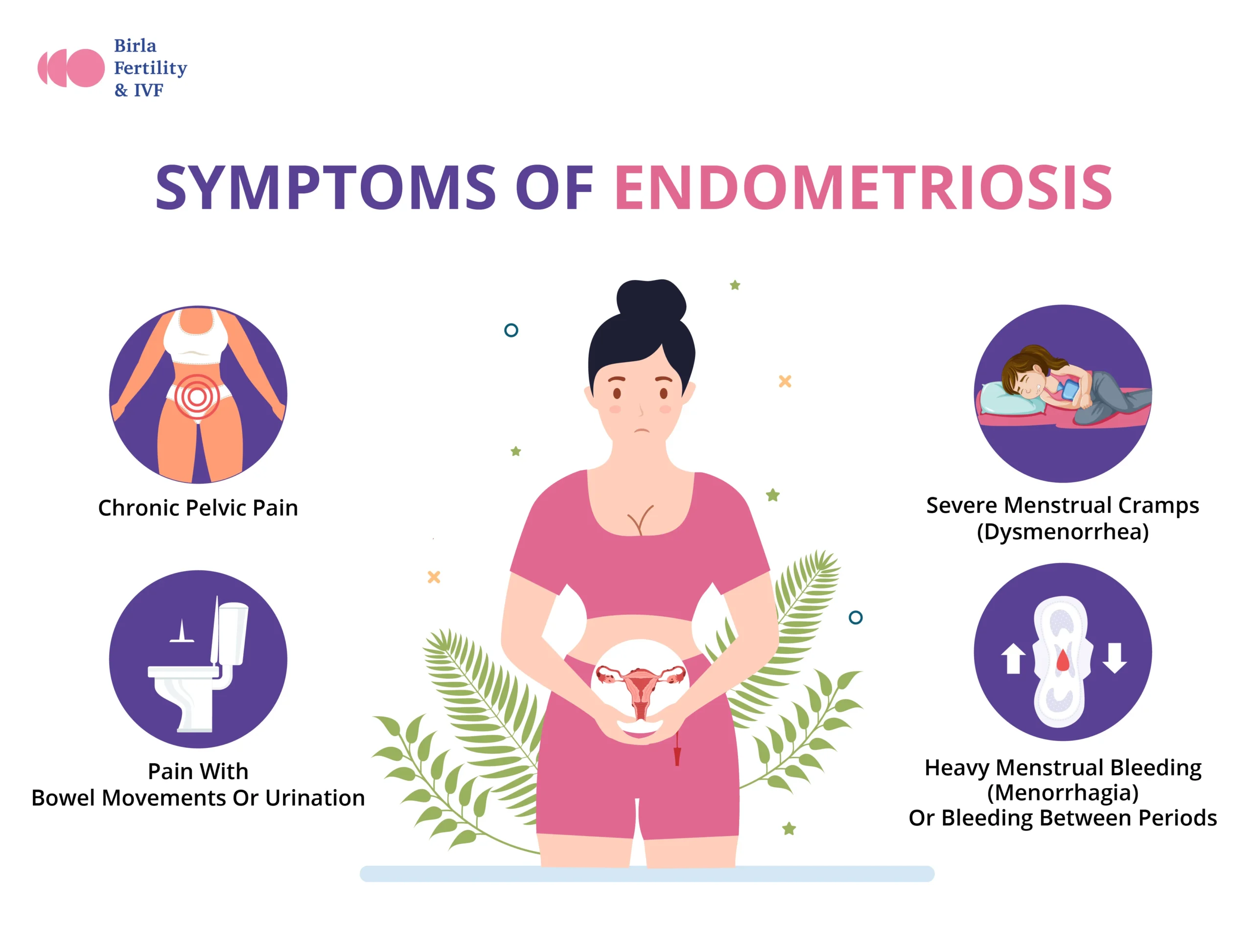
Endometriosis is a chronic condition in which endometrium—tissue lining inside the uterus—grows outside the uterus. Such abnormal tissue growth can be found down on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, the external surface of the uterus, and different organs inside the pelvis. Endometriosis is a painful gynaecological disorder that affects more than 190 million girls and women worldwide. India alone bears 25% of the burden, with an estimated 43 million women suffering from this painful disorder. According to the Endometriosis Foundation of America, it affects about 1 in 10 women of reproductive age.
Symptoms of Endometriosis:
What is PCOS?
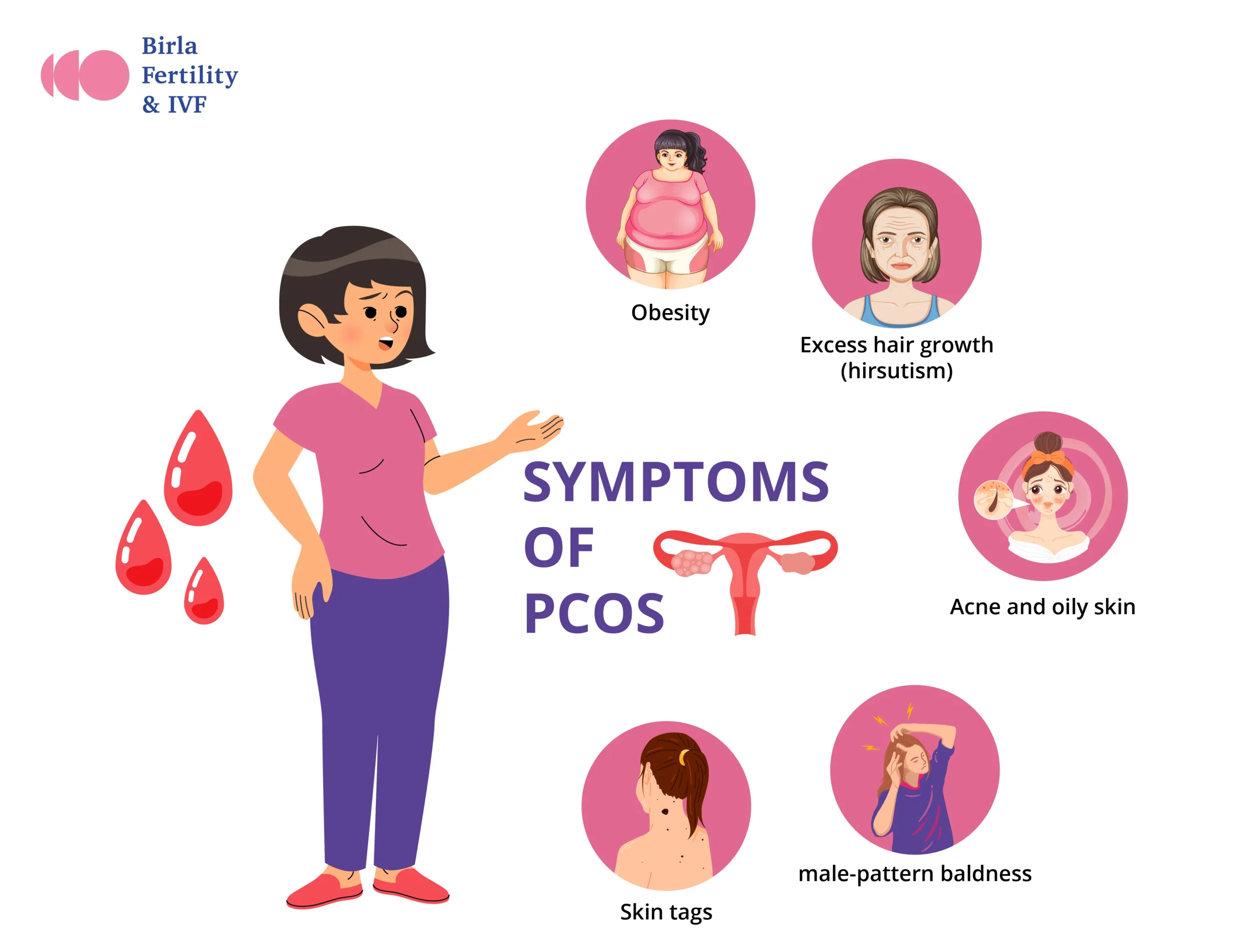
Among women of reproductive age, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder. According to the World Health Organization <(WHO), PCOS affects approximately 8-13% of women of reproductive age, with up to 70% of instances going untreated. In addition, women with PCOS may experience excessive levels of male hormones (androgens) or have irregular or prolonged periods. As a result, the ovaries may develop numerous small fluid-filled sacs, also referred to as cysts, leading to the failure to release eggs regularly and causing infertility.
Symptoms of PCOS:
Difference Between PCOS and Endometriosis
The below-table shows the significant differences in symptoms between PCOS and Endometriosis:
| Symptom | Endometriosis | PCOS |
| Menstrual Irregularities | Heavy and painful periods | Irregular or missed periods |
| Pain | Severe menstrual cramps, chronic pelvic pain, pain during intercourse | Pelvic discomfort (less common) |
| Fertility Issues | Infertility due to endometrial tissue causing blockages and inflammation | Infertility due to irregular ovulation or anovulation |
| Hormonal Imbalance | Not a primary cause, managed with hormonal treatments | Elevated androgens, insulin resistance |
| Ovarian Appearance | Endometriomas (chocolate cysts) | Enlarged ovaries with multiple small follicles |
| Skin Issues | Not common | Acne, oily skin, skin tags, dark patches |
| Hair Growth | Not a primary symptom | Excess hair growth (hirsutism), thinning hair |
| Weight Issues | Not common | Obesity and difficulty losing weight |
Causes and Risk Factors
Although the exact cause of endometriosis is unknown, there are a number of theories, some of which include retrograde menstruation, disorders of the immune system, and genetic factors. Women who have had endometriosis in their families are more likely to get it
For PCOS also, the root cause is unknown, but it is thought to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Insulin resistance, increased androgen levels, and low-grade inflammation are common characteristics of PCOS. Women with a family history of PCOS are at a higher risk of developing the condition.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Endometriosis:
Endometriosis is often diagnosed with a pelvic exam, ultrasound, or laparoscopy. Treatment options differ according to the severity of the symptoms and the patient’s desire to conceive. They include:
- Pain medication
- Hormonal therapies (like birth control pills or GnRH agonists)
- Surgical intervention to remove endometrial tissue
PCOS:
PCOS is diagnosed using a medical history, physical exams, blood tests to detect hormone levels and ovarian ultrasound imaging tests. Treatment focuses mostly on treating symptoms and may include:
- Lifestyle changes (such as diet and exercise)
- Medications to regulate menstrual cycles (like birth control pills)
- Fertility treatments (like IVF and IUI)
- Therapies to manage insulin levels or hair growth
Conclusion
It is crucial to understand the differences between endometriosis and PCOS for effective diagnosis and treatment. Both conditions can have a profound impact on a woman’s quality of life and overall fertility health. If you suspect or are diagnosed with either condition, it is important to consult with a specialist for an accurate diagnosis and customised treatment plan according to your requirements. Awareness of such disorders and early intervention can help manage symptoms and improve outcomes for women. Furthermore, if you are affected by any of these conditions and seeking fertility treatment, contact us by calling the mentioned number. Or, by filling in the given form with the required details to book an appointment with our fertility specialist for the right guidance.
Our Fertility Specialists
Related Blogs
To know more
Birla Fertility & IVF aims at transforming the future of fertility globally, through outstanding clinical outcomes, research, innovation and compassionate care.
Had an IVF Failure?
Talk to our fertility experts

 Our Centers
Our Centers
















