Sperm Donation
Sperm donation is a medical procedure that helps couples dealing with infertility. A carefully selected donor provides a semen sample that can be used in various assisted reproductive technologies like Intrauterine Insemination (IUI), In Vitro Fertilization (IVF), Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI). Not anyone can donate sperm as sperm donation involves rigorous screening of donors to ensure genetic, physical, and mental fitness. The donated sperm is cryopreserved for use in assisted reproductive treatments.

Medical Procedures
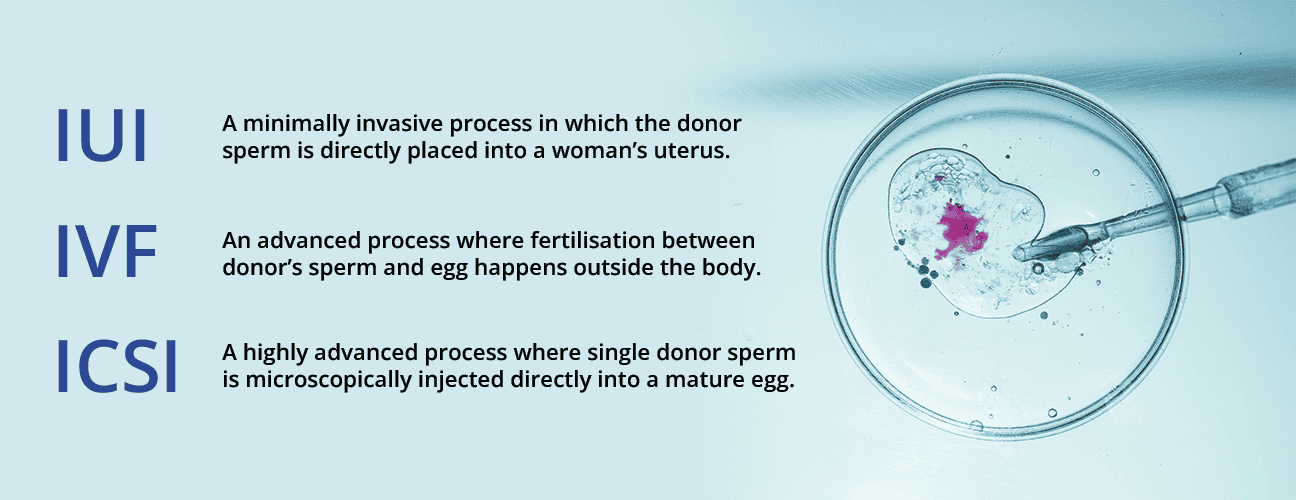
Three primary assisted reproductive technologies leverage donor sperm, each with unique approaches to helping individuals achieve their dream of parenthood.
Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): A precise and minimally invasive procedure where carefully selected donor sperm is directly placed into the woman’s uterus during her most fertile period. This technique maximizes the potential for natural fertilization by strategically positioning high-quality sperm closer to the egg, increasing the chances of successful conception.
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): A more complex approach where donor sperm fertilizes eggs outside the body in a controlled laboratory environment. Eggs are carefully retrieved and combined with donor sperm, allowing embryologists to monitor fertilization and select the most viable embryos for transfer. This method provides greater control and insight into the early stages of potential pregnancy.
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI): The most advanced technique, where a single donor sperm is microscopically injected directly into a mature egg. This method is particularly effective for addressing severe male factor infertility, ensuring precise sperm selection and maximizing the potential for successful fertilization when traditional methods may not be viable.
Benefit From Sperm Donation
Medical Scenarios:
- Men with extremely low sperm count (oligospermia) or poor sperm motility (asthenozoospermia).
- Couples where the male partner has azoospermia (complete absence of sperm) or testicular failure.
- Couples with genetic disorders or chromosomal abnormalities risking hereditary transmission of severe medical conditions.
- Men with obstructive or non-obstructive causes of infertility, including prior medical treatments (e.g., chemotherapy, radiation therapy) leading to sperm production failure.
- Situations involving Rh incompatibility where the male partner’s blood type poses risks to the pregnancy.
- Severe sexual dysfunction, where natural conception is challenging.
Personal Scenarios:
- Couples where the male partner has irreversible or unexplained fertility issues.
- Single women desiring biological motherhood through assisted reproductive techniques (ART).
- Same-sex female couples who wish to conceive and start a family.
- Widowed women looking to pursue motherhood after losing their partner.
- Women in situations where their male partner has undergone vasectomy or sterilization but no longer wishes to undergo reversal.
- Couples who have experienced multiple failed IVF cycles or ICSI attempts with the male partner’s sperm and are exploring alternative solutions.

How to Become a Sperm Donor
Becoming a sperm donor is a rigorous process with stringent eligibility criteria:
Basic Demographic Requirements for Sperm Donation
- Age Range: 18 to 40 years (most banks prefer 18-35)
- Physical Health: Excellent overall condition
- Lifestyle: Non-smoker, no drug use
- Minimum sperm count: 15 million per milliliter
- At least 40% sperm motility
- Normal sperm morphology
- No family history of genetic disorders
Cost of Sperm Donation
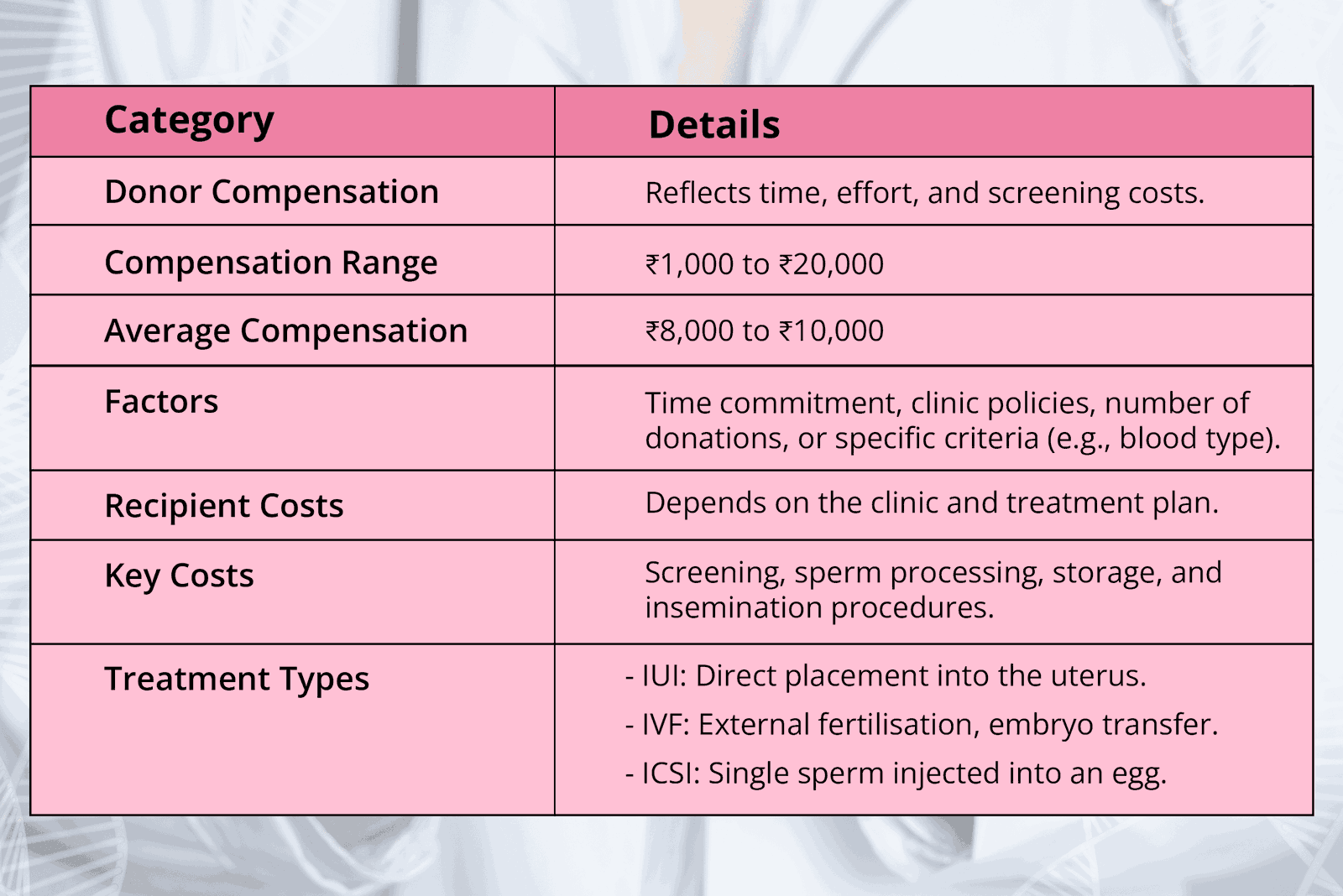
1. Donor Compensation
Donor compensation reflects the time, effort, and associated medical screening costs incurred during the sperm donation process. This ensures that donors are fairly compensated for their commitment to the process.
- Compensation Range For Sperm Donors: ₹1,000 to ₹20,000
- Average Compensation For Sperm Donors: ₹8,000 to ₹10,000
The compensation amount may vary depending on factors such as:
- The donor’s time commitment during the screening, donation, and follow-up process.
- The fertility clinic’s policies and the specific requirements of the program.
- The number of donations made or the clinic’s need for certain donor criteria (e.g., specific blood type, educational background, etc.).
2. Recipient Costs
The cost of fertility treatments involving donor sperm can differ significantly based on the chosen clinic and the type of treatment plan. Recipient costs typically encompass several key components:
- Medical Screening and Testing: Ensuring donor sperm is healthy and free of infectious diseases. This includes genetic screening, blood tests, and semen analysis.
- Processing and Storage: Preparation of the sperm sample for insemination (e.g., washing, freezing, and cryopreservation to maintain viability).
- Insemination Procedure: Costs may vary depending on the type of fertility treatment chosen whether it is IUI. IVF or ICSI.
Tests Required For Sperm Donation
- Medical History Evaluation
- Two-generation family medical history review
- Identifying potential hereditary conditions
- Physical Examination
- Complete health assessment
- Checking for any underlying health conditions
- Comprehensive Testing
- Blood tests for genetic disorders
- Screening for infectious diseases
- Tests for HIV, Hepatitis B/C, Syphilis
- Genetic carrier screening
- Psychological Evaluation
- Mental health assessment
- Understanding long-term psychological implications
Why Choose Us
Choosing the right fertility clinic is crucial for starting your family. At Birla Fertility & IVF, we offer personalised care with expert specialists guiding you every step of the way. Our advanced labs and outstanding success rates have helped over 2,30,000 patients achieve their dream of parenthood.
Frequently Asked Questions
Recent Blogs
Book an appointment
Hassle-Free Appointment Booking
Select Preferences
I know my doctor
Sperm Freezing Cost in Different Cities
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Jalandhar
- Sperm Freezing Cost in India
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Kozhikode
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Thrissur
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Bangalore
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Bhopal
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Bhubaneswar
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Nagpur
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Meerut
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Kannur
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Allahabad
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Cuttack
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Rewari
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Siliguri
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Perinthalmanna
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Patna
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Chennai
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Vijayapura
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Mumbai
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Kolar
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Salem
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Palakkad
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Mangalore
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Indore
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Hyderabad
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Jaipur
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Raipur
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Guwahati
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Chandigarh
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Ranchi
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Ahmedabad
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Surat
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Howrah
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Kolkata
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Noida
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Gorakhpur
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Varanasi
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Lucknow
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Gurgaon
- Sperm Freezing Cost in Delhi

 Our Centers
Our Centers