Tubal Patency Tests
A tubal patency test is a diagnostic procedure used to evaluate the openness and function of a woman’s fallopian tubes. The test results help guide treatment options, such as pursuing in-vitro fertilisation if the tubes are blocked. Birla Fertility & IVF offers these advanced tubal patency testing services as part of their comprehensive infertility treatment offerings at their clinics.

What is Tubal Patency Test?
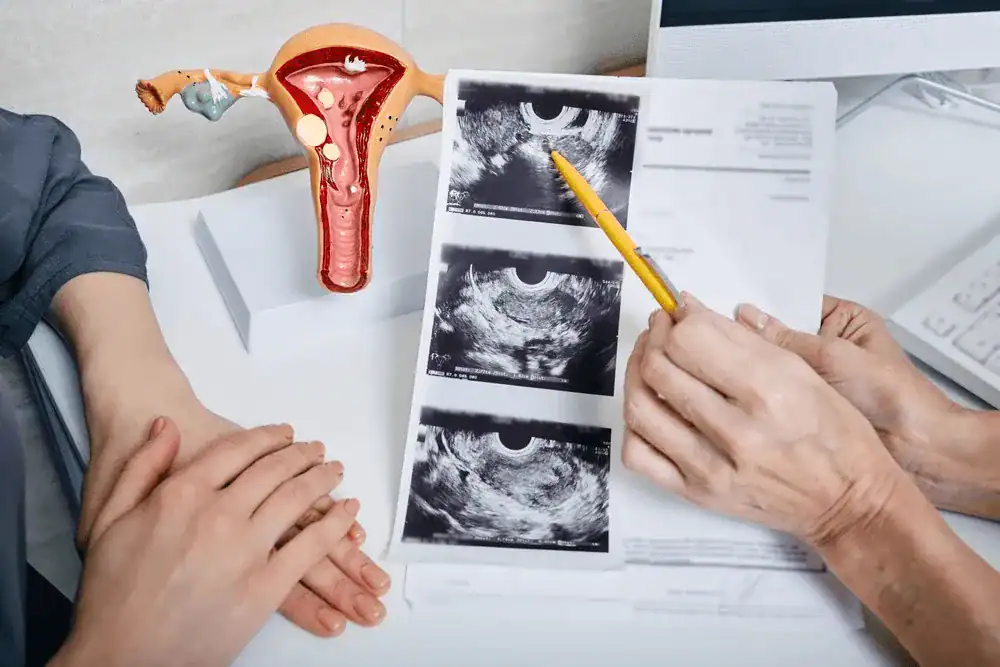
The fallopian tubes are crucial for fertility, carrying the egg from the ovary to the uterus for fertilisation. Blocked or damaged tubes can cause infertility, which is why the tubal patency test is performed. It helps to check if the tubes are open and functioning normally. This test also helps to check the following conditions:
- Primary or secondary infertility
- Recurrent miscarriage
- Evaluation before a new assisted reproductive treatment cycle
- Sterilisation assessment
- Congenital anomalies or anatomic variants affecting the fallopian tubes
In summary, checking tubal patency is a critical step in evaluating female infertility.
Why is the Tubal Patency Test Performed?
The tubal patency test assesses the health and function of a woman’s fallopian tubes.
The main reasons for conducting this test are:
- Ensure the tubes are clear before starting treatments like IVF.
- To investigate infertility in couples who haven’t conceived after a year of regular intercourse.
- To confirm the success of tubal ligation reversal.
- After conditions like pelvic inflammatory disease or endometriosis, which can harm the tubes.
- To rule out tubal causes of infertility.

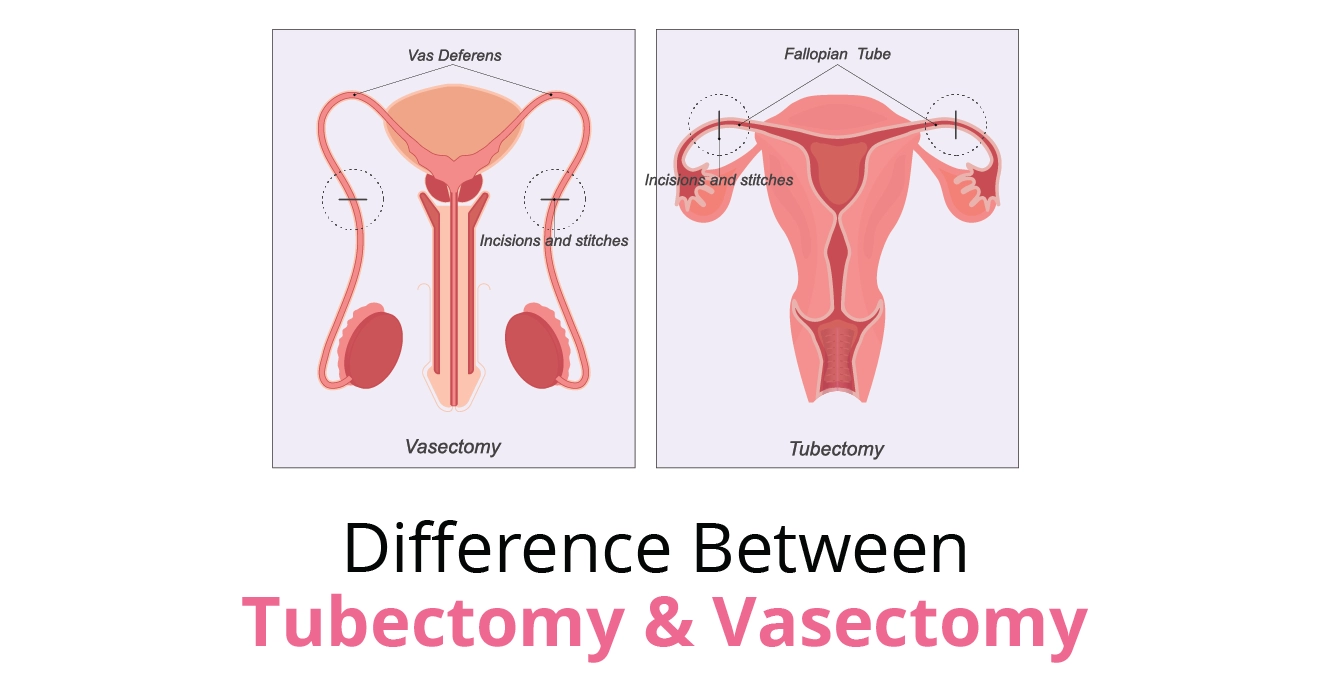
Types of Tubal Patency Test

Tubal patency tests are diagnostic procedures used to assess the health and function of a woman’s fallopian tubes, which play a crucial role in fertility. The main tubal patency tests include:
-
Hysterosalpingography (HSG): It is an X-ray-based test in which a dye is injected through the cervix to visualise the uterus and fallopian tubes. This is done to check for any blockages or abnormalities.
-
Sonosalpingography (SSG) or Hysterosalpingo-Contrast Sonography (HyCoSy): An ultrasound-based test that uses fluid injected through the cervix to assess tubal patency. It allows the doctor to see the path of the fluid and identify any blockages.
-
Laparoscopy with Chromopertubation: Considered the “gold standard”, this minimally invasive surgical procedure directly examines the fallopian tubes. It is done by injecting a dye through the cervix to check for patency.
-
Sonosalpingography with Saline Infusion (SIS): It involves injecting a saline solution through the cervix. This is done while using transvaginal ultrasound to visualise the uterine cavity and check tubal patency.
-
Doppler Hysterosalpingography: It is a diagnostic technique that combines HSG with colour Doppler ultrasonography. It assesses tubal patency and blood flow in the fallopian tubes.
These tests are typically performed during the first half of the menstrual cycle, as it is important to avoid any potential pregnancy. The choice of test depends on factors like the patient’s history, diagnosis, and physician preference.
Why Choose Us
Choosing the right fertility clinic is crucial for starting your family. At Birla Fertility & IVF, we offer personalised care with expert specialists guiding you every step of the way. Our advanced labs and outstanding success rates have helped over 2,30,000 patients achieve their dream of parenthood.
Outcomes of Tubal Patency Test
Normal Tubal Patency
- If both fallopian tubes are open and unobstructed, it indicates normal tubal function. Women with normal tubal patency have a 30%–50% chance of natural conception per cycle.
Unilateral Tubal Blockage
- If one fallopian tube is blocked while the other is open, it is known as unilateral tubal occlusion. Pregnancy is still possible with one open tube, but the chance is reduced by about 10%–15%.
Bilateral Tubal Blockage
- If both fallopian tubes are blocked, it is called bilateral tubal occlusion. Bilateral tubal blockage is a major cause of infertility, accounting for about 30% of female infertility cases.
Frequently Asked Questions
Recent Blogs
Book an appointment
Hassle-Free Appointment Booking
Select Preferences
I know my doctor
HSG Cost in Different Cities
- HSG Test Price in India
- HSG Test Cost in Jalandhar
- HSG Test Cost in Chandigarh
- HSG Test Cost in Siliguri
- HSG Test Cost in Perinthalmanna
- HSG Test Cost in Patna
- HSG Test Cost in Chennai
- HSG Test Cost in Vijayapura
- HSG Test Cost in Mumbai
- HSG Test Cost in Kolar
- HSG Test Cost in Bangalore
- HSG Test Cost in Thrissur
- HSG Test Cost in Salem
- HSG Test Cost in Palakkad
- HSG Test Cost in Mangalore
- HSG Test Cost in Kannur
- HSG Test Cost in Kozhikode
- HSG Test Cost in Bhopal
- HSG Test Cost in Indore
- HSG Test Cost in Hyderabad
- HSG Test Cost in Nagpur
- HSG Test Cost in Jaipur
- HSG Test Cost in Raipur
- HSG Test Cost in Guwahati
- HSG Test Cost in Ranchi
- HSG Test Cost in Ahmedabad
- HSG Test Cost in Surat
- HSG Test Cost in Cuttack
- HSG Test Cost in Bhubaneswar
- HSG Test Cost in Howrah
- HSG Test Cost in Kolkata
- HSG Test Cost in Meerut
- HSG Test Cost in Allahabad
- HSG Test Cost in Noida
- HSG Test Cost in Gorakhpur
- HSG Test Cost in Varanasi
- HSG Test Cost in Lucknow
- HSG Test Cost in Rewari
- HSG Test Cost in Delhi

 Our Centers
Our Centers