Early Menopause: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment Options

Table of Contents
- What is Premenopause?
- At What Age does Menopause Start?
- Causes of Early Menopause
- Symptoms of Premature Menopause
- Menopause Diagnosis
- Treatment Options for Early Menopause
- Risks Associated with Early Menopause
- Relationship Between Early Menopause and Fertility
- Lifestyle Modifications to Ease the Transition
- Difference Between Menopause & Premature Menopause
- Can Premature Menopause Be Reversed?
- Bleeding after menopause
- Can you get pregnant post menopause?
- Conclusion
- FAQs :
- What happens during menopause?
- What are the three stages of menopause?
- What are the first signs of menopause?
- What are the symptoms of perimenopause at 44?
- How do I know if I am going through early or premature menopause?
- What is the best treatment for early menopause?
- What is the biggest symptom of menopause?
Menopause is a natural biological process that marks the end of a woman’s reproductive years. It typically occurs between the ages of 45 to 55. However, at times, a lot of women experience symptoms associated with menopause (hot flashes, night sweats, sleep problems, low energy, and joint pain) before the age of 40. This is known as early menopause. This blog will cover the causes, symptoms, and treatment options around the same time.
What is Premenopause?
Premenopause is the phase before menopause when hormonal levels begin to fluctuate, but periods are still occurring. Women may notice changes like irregular cycles, mood swings, sleep disturbances, or reduced fertility. This stage can start several years before menopause and varies widely from woman to woman. There can be various reasons for the same, stemming from a combination of medical, genetic, and lifestyle factors.
As per the National Institute of Health (NIH),
- Early menopause or premature menopause affects 1% of women under the age of 40
- Causes of early menopause may differ; it might be a subtle indication of other developing neuro, psychological, ortho, or cardiac comorbidities.
- With the early onset of menopause symptoms, the risk of infertility soars up.
In this article, let’s explore the key causes of early menopause, its symptoms, and treatment options to ease this challenging transition.
At What Age does Menopause Start?
Many women wonder at what age menopause starts. As mentioned earlier, the natural menopause age range is usually 45 to 55 years. Globally, the average is around 51 years. Early menopause can happen before age 45. On the other hand, premature menopause occurs before the age of 40.
Menstrual cycles come to a stop with menopause, which is verified after 12 months without periods.
Causes of Early Menopause
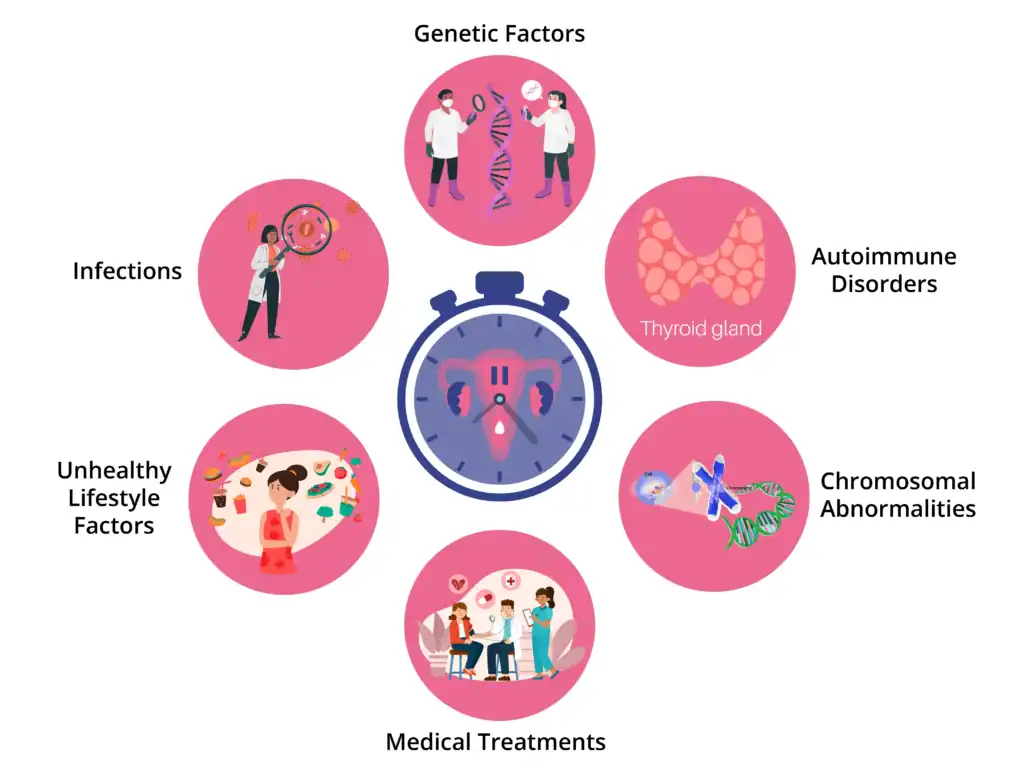
The causes of early menopause may vary from one individual to another, depending on their age and underlying condition. For women, transitioning into this phase can be challenging. Hence, it may lead to significant implications for their overall health and fertility. Some of the common causes of early menopause are:
- Genetic Factors: It is a significant cause of early menopause. For example, if a woman’s mother or sibling went through early menopause, there is a higher likelihood that she might get it too.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and thyroid disease can cause the immune system to attack the ovaries, resulting in early menopause.
- Medical Treatments: Chemotherapy and radiation therapy for cancer can harm the ovaries and cause early menopause. Additionally, surgeries for the ovaries or uterus removal can cause early menopause.
- Chromosomal Abnormalities: Turner syndrome and Fragile X syndrome are genetic disorders that cause premature ovarian failure, leading to early menopause.
- Unhealthy Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle may accelerate the onset of menopause. High levels of stress and inadequate nutrition are also major causes of early menopause.
- Infections: Certain infections, such as mumps, tuberculosis, and malaria, have been linked to early menopause or premature ovarian failure.
Symptoms of Premature Menopause
Some symptoms of premature menopause can impact the quality of life, causing significant discomfort as well. Some of the common early menopause symptoms are:
- Irregular Periods– Changes in menstrual cycle patterns, such as irregular or missed periods, and one of the early indications of menopause.
- Hot Flashes & Night Sweats- There are sudden sensations of heat, particularly at night. This can impair sleep.
- Mood Changes- You can feel irritation, anxiety, or depression during early menopause.
- Vaginal Dryness- Low estrogen levels can cause dryness, discomfort, and pain during intercourse.
- Decreased Libido- Lower sex drive is one of the most common symptoms of early menopause.
- Cognitive Changes- There is a high possibility of developing memory-related problems and having difficulty concentrating.
- Sudden Bodily Changes- Irregular weight gain or weight loss, along with thinning hair and dry skin, are also associated with early menopause.
Menopause Diagnosis
The only way to get confirmation is through a formal diagnosis. Before you consult a doctor, try tracking your periods. The uneven pattern will serve as an additional clue for your doctor.
A gynaecologist may recommend tests to determine the levels of:
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)- When a woman is approaching menopause, the FSH increases. Hence, it can serve as an indicator for diagnosis.
- Estradiol- The level of Estradiol tells how much estrogen is being produced by your ovaries. During menopause, estradiol levels decrease.
- Thyroid hormones– Next, check the thyroid levels since some of the problems with the thyroid gland cause symptoms that mimic menopause.
- Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH)– This test indicates your ovarian reserve. Lower AMH levels can signal reduced egg supply and help assess menopausal onset.
In case you have missed your period for 12 consecutive months, then it confirms your diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Early Menopause
Here are a few common treatment options that can help you manage early menopause:
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): The most often prescribed treatment for menopausal symptoms is hormone replacement therapy (HRT). It helps replenish your body’s oestrogen, which starts to decline around menopause. Other hormones that your body is no longer manufacturing, such as progesterone and testosterone, may also be necessary at times.
- Non-Hormonal Medications: Antidepressants and anti-seizure medications are prescribed for symptoms of early menopause and are effective in managing hot flashes and mood swings.
- Vaginal Estrogen: For vaginal dryness and discomfort, doctors recommend low-dose estrogen, which can be applied directly to the vaginal area through creams, tablets, or rings.
- Bone Health Management: To prevent osteoporosis, calcium and vitamin D supplements, along with medications like bisphosphonates, may be recommended.
- Herbal Remedies: Some women find relief with herbal supplements like black cohosh, evening primrose oil, and red clover. However, no research proves it, so it is essential to consult with your doctor before starting any herbal treatment.
Risks Associated with Early Menopause
There are some risks associated with early menopause:
- Infertility– The most common risk is that early menopause stops ovulation, which makes natural conception impossible. However, there are assisted fertility treatments that can help before you hit menopause, like egg or embryo freezing.
- Bone loss– Estrogen is the hormone that protects bone density. When early menopause happens, it leads to faster bone thinning, and there is a higher risk of fractures because of the same.
- Cardiovascular problems– Estrogen also plays a role in maintaining heart and blood vessel health. Without it, women usually face a higher risk of heart disease, stroke, and hypertension.
- Cognitive decline– Early menopause can lead to hormonal changes that can affect brain function. This can lead to memory problems, dementia, or Alzheimer’s later in life.
- Reduced life expectancy– There is research that suggests that women with early menopause live shorter lives.
Relationship Between Early Menopause and Fertility
Early menopause, once triggered, can significantly impact fertility as it leads to a decrease in the number and quality of eggs. Women experiencing early menopause may face challenges conceiving naturally. However, there are options available:
- Egg Freezing– This is one of the most talked-about techniques of fertility preservation, allowing women to freeze their eggs beforehand for use later in life.
- Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)- Options like in vitro fertilisation (IVF) combined with donor eggs can be an effective treatment method for women with early menopause.
- Surrogacy– Surrogacy and adoption are two viable options for women affected by early menopause.
Lifestyle Modifications to Ease the Transition
For most women, particularly those who start the phase early, transitioning into menopause can be difficult. However, you can reduce discomfort by making a few easy lifestyle changes, some of which are as follows:
- Balanced Diet- Protect your body from nutrient depletion by following your healthy diet rich in calcium, vitamin D, and phytoestrogens can help manage this effectively. Food items such as leafy greens, dairy products, and soy are beneficial for women experiencing early menopause.
- Regular Exercise– Adding exercise to your routine can help lower stress and elevate mood in addition to helping maintain a healthy body mass index (BMI). Weight-bearing exercises are also beneficial for bone health.
- No Smoking– Quitting smoking can lessen the symptoms of early menopause and postpone the beginning of menopause.
- Stress Management- Practising yoga, meditation, and deep-breathing exercises can help alleviate stress and improve overall well-being.
- Adequate Sleep- One should concentrate in having a good sleep routine and creating a comfortable sleep environment can help you manage night sweats and improve your sleep quality.
Difference Between Menopause & Premature Menopause
Menopause-
Menopause occurs earlier than expected, between the ages of 40-45. It can be caused by factors related to family medical history or genetics. There are certain medical treatments as well that can cause early menopause, such as surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation. The symptoms are similar to natural menopause, including hot flashes, mood changes, vaginal dryness, and irregular periods. There are other health risks involved as well, like reduced bone density (also known as osteoporosis) and loss of estrogen, resulting in a higher risk of heart disease.
Premature Menopause-
Menopause occurs before the age of 40. It can be caused due to several reasons, including genetic or chromosomal abnormalities, autoimmune diseases, and some cancer treatments that affect the ovaries. The symptoms are more sudden and severe, as estrogen drops at a very young age. Some women may even notice signs of early menopause in their 20s, such as irregular cycles or hot flashes, which indicate POI.
Can Premature Menopause Be Reversed?
No, there is no certain way to reverse premature menopause that happens before the age of 40. It is because the ovaries quit working way earlier than anticipated. This results in infertility and decreased estrogen production.
There are treatments available that help control symptoms and improve quality of life. Here are some of the popular options:
- Hormone Replacement Therapy- HRT is a common medical technology that helps lower the risk of heart disease and relieves symptoms like hot flashes.
- Supplements- Calcium and vitamin D supplements help maintain bone density and prevent osteoporosis.
- Non-Hormonal Mediation- There are some antidepressants that can lessen women’s mood swings and hot flashes.
- Vaginal Estrogen- These are available in the form of tablets, rings, or lotions to ease urinary symptoms, dryness, and discomfort in the vagina.
As we already mentioned earlier, fertility therapies like IVF can help women conceive despite premature menopause. Apart from medical treatment, positive lifestyle changes, such as stress reduction, regular exercise, and a balanced diet, also help promote overall well-being. Even though premature menopause cannot be reversed, there is prompt medical attention can help to adjust to this transition, both mentally and physically.
Bleeding after menopause
A lot of women ask if it is normal to have bleeding after menopause. It can be a sign of a serious issue, especailly if it occurs after a year since your last period. This condition can show the symptoms of polyps (noncancerous growth), uterine cancer, or vaginal dryness. Bleeding after menopause requires medical attention and suitable treatment.
Can you get pregnant post menopause?
Even though your ovaries stop releasing eggs after menopause, it doesn’t mean that your dream of becoming a mother is over. We understand that your reproductive system might not work the same way, but there are assisted reproductive treatments that can make parenthood possible.
One option is a donor egg combined with IVF (In Vitro Fertilisation). In this option, a donor’s eggs are fertilised with your partner’s sperm in the lab, and the result, as an embryo, is placed in your uterus. It is one of the popular ways that has helped many women become parents post menopause.
There is one more possibility. Nowadays, many women are freezing their eggs earlier in life. In this process, the eggs are frozen and, when needed, thawed for IVF. There may be a few complications, but doctors keep a close eye throughout the journey to help you with them. The key is to talk to a fertility specialist and know all your options. They can guide you with advice that’s right for you and your parenthood journey.
Conclusion
Early menopause is a significant gynecological condition that can bring a challenging transition. Experiencing it can be confusing and overwhelming, as it affects hormone levels, fertility, and overall well-being. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments can help women manage this phase more effectively.
To combat symptoms of early menopause, adopting a healthy lifestyle, seeking appropriate medical treatments, and staying informed can be very helpful. Medical interventions such as HRT (Hormone Replacement Therapy) can make a significant difference. They can help you take the first step in taking control and managing this transition with confidence. Medical interventions such as HRT (Hormone Replacement Therapy) can make a significant difference. So, what are you waiting for? Connect with our specialists to know more!
FAQs :
What happens during menopause?
It is a time when your body stops producing estrogen and progesterone. This can leave you feeling fatigued, moody, and experiencing hot flashes.
What are the three stages of menopause?
Women undergo three stages of menopause: perimenopause, menopause, and postmenopause.
What are the first signs of menopause?
The first signs of menopause include sore breasts, trouble sleeping, vaginal dryness, missed or irregular periods, and mood changes.
What are the symptoms of perimenopause at 44?
There can be different symptoms of perimenopause at 44, which mostly include irregular periods (shorter, longer, heavier, or skipped cycles), hot flashes, and night sweats, along with trouble falling or staying asleep. You will also go through different mood changes which including fatigue and low energy.
How do I know if I am going through early or premature menopause?
Early or premature menopause may be suspected if your periods stop or become very irregular before age 45 (early) or before 40 (premature), along with symptoms like hot flashes and night sweats. A gynecologist can confirm it based on your menstrual history and hormone tests (such as FSH) and rule out other causes.
What is the best treatment for early menopause?
The most effective treatment for early menopause is hormone replacement therapy (HRT) to replace estrogen (and progesterone if the uterus is present) until the natural menopause age, unless medically contraindicated. Alongside this, lifestyle changes, calcium, vitamin D, and regular medical follow-up help protect bone and heart health, as well as overall health.
What is the biggest symptom of menopause?
The most common and noticeable symptom of menopause is hot flashes, often with night sweats. They’re caused by hormonal changes and can affect sleep, mood, and daily comfort.
Our Fertility Specialists
Related Blogs
To know more
Birla Fertility & IVF aims at transforming the future of fertility globally, through outstanding clinical outcomes, research, innovation and compassionate care.
Had an IVF Failure?
Talk to our fertility experts

 Our Centers
Our Centers


















