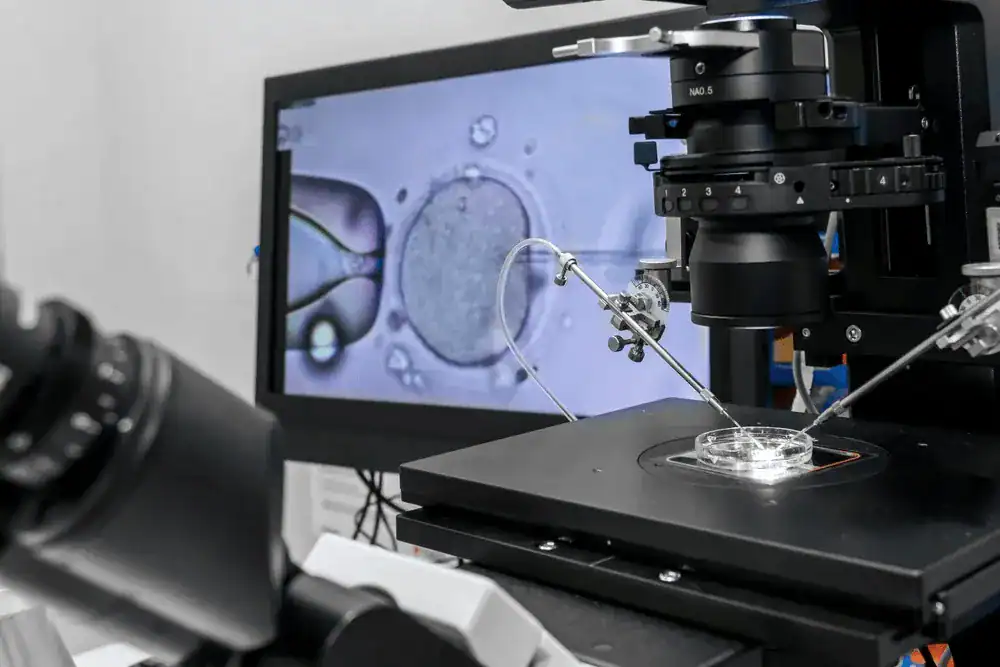
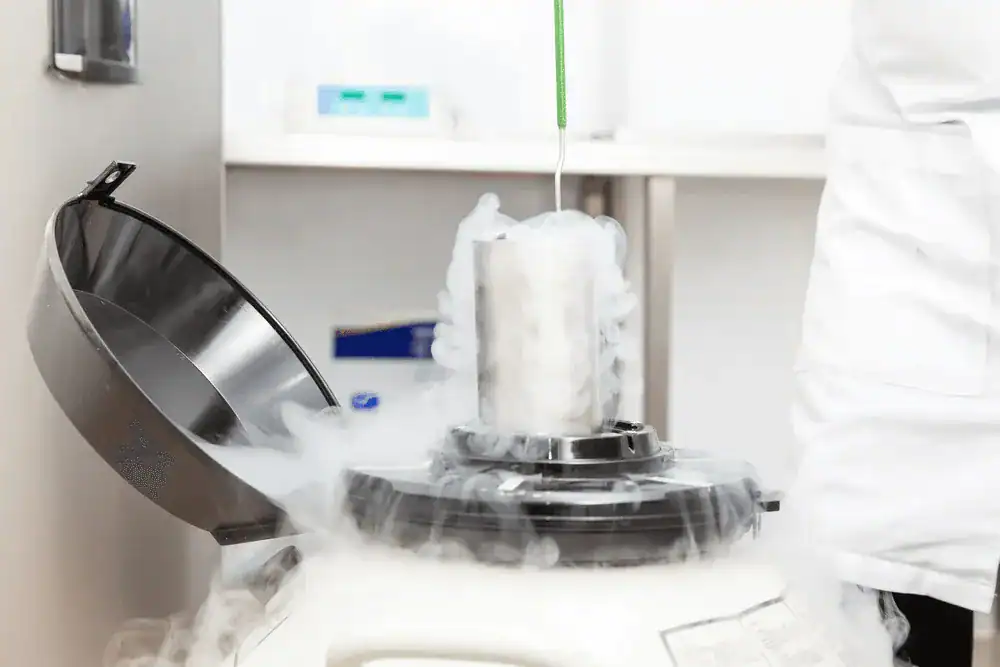
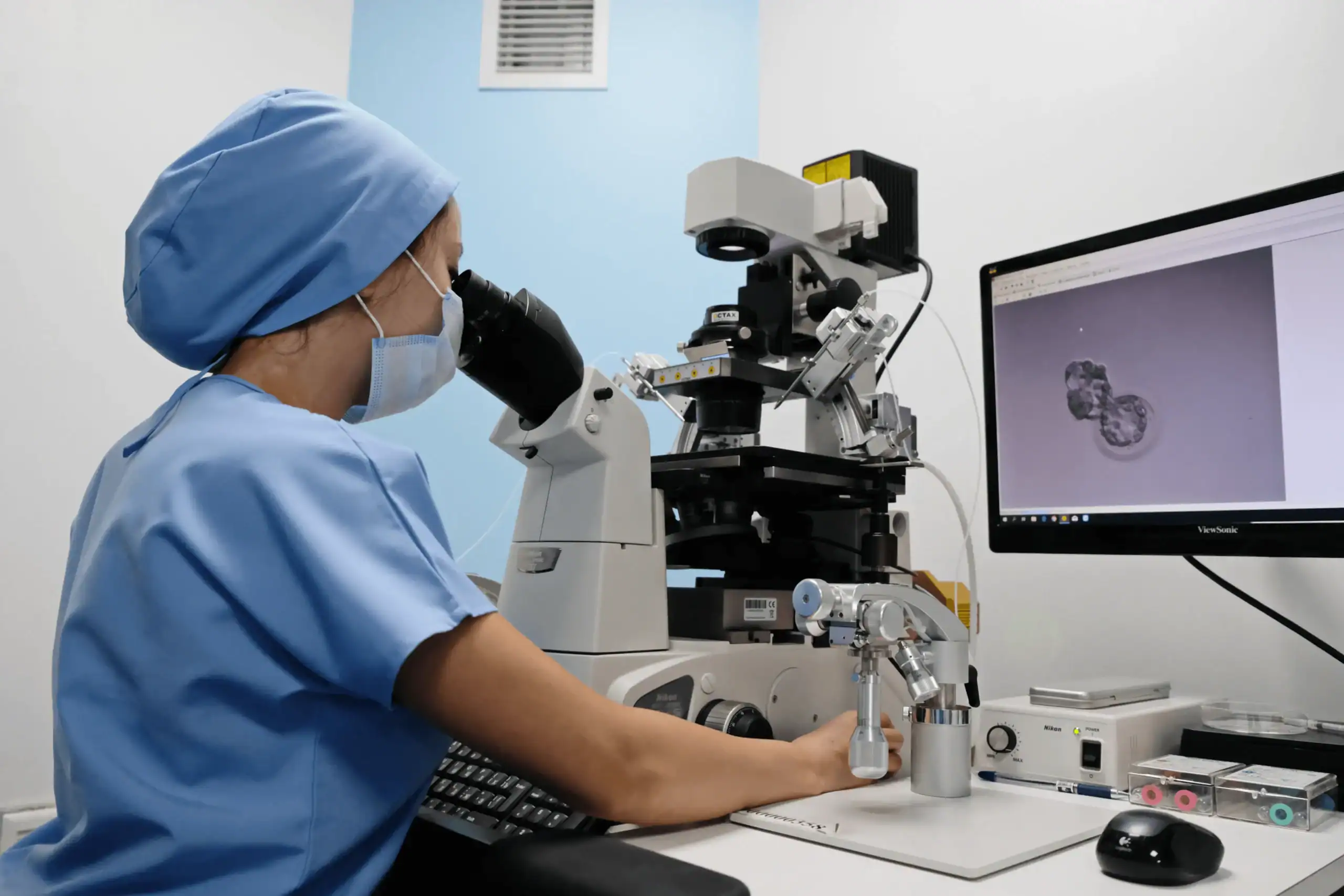
Understanding Infertility
Infertility is the inability to conceive after one year of regular unprotected intercourse. It affects individuals emotionally and socially. It can strain relationships, cause anxiety, and affect self-esteem. Globally, 1 in 6 couples face infertility challenges. According to a report, 10-15% of married couples in India have experienced infertility at some point. Primary infertility is when no pregnancy has occurred, while secondary infertility refers to difficulties after a previous pregnancy. Understanding the crucial elements of conception or fertility such as ovulation, sperm quality and quantity, uterine health, fallopian tube patency, and hormonal balance is vital for managing infertility.

Types of Infertility
Infertility can be broadly categorised into:
- Primary Infertility: Inability to achieve pregnancy after 12 months of unprotected intercourse. It may result from anatomical, hormonal, or genetic factors attributable to either of the partners or both.
- Secondary Infertility: Occurs when a couple has had a previous pregnancy but struggles to conceive again. Its causes can include age-related decline in fertility, previous infections, or changes in reproductive health.
- Unexplained Infertility: Characterised by the absence of an identifiable cause despite thorough diagnostic testing. Finding treatment options is challenging as the underlying reasons for infertility remain unknown.
Causes of Infertility
In Women
- Age: Decline in ovarian reserve and egg quality as women age.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOs): Hormonal disorder leading to irregular or no ovulation.
- Blocked or Damaged Fallopian Tubes: Prevents sperm from reaching the egg or hampers implantation of the fertilised egg.
- Uterine Fibroids and Polyps: Interfere with embryo implantation and development by distorting the uterine cavity.
- Hormonal Imbalance: Thyroid disorders or high prolactin levels affect ovulation and fertility.
- Chromosomal Abnormalities: Genetic variations affecting reproductive health.
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): Infections causing inflammation and scarring of reproductive organs.
In Men
- Infections: Chronic infections such as sexually transmitted infections can damage the male reproductive organs, affecting sperm production.
- Erectile Dysfunction: Difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection or premature ejaculation impact fertility.
- Varicocele: Enlargement of veins within the scrotum impairs sperm production and quality.
Genetic Disorders: Klinefelter Syndrome, where males are born with an extra X chromosome, affects testicular development and sperm production.
Diagnosis of Infertility
Diagnosis of Female Infertility
To customise treatment, your infertility specialist begins by reviewing previous reports and recommending specific tests. The comprehensive evaluation will help identify any underlying issues affecting a woman’s ability to conceive:
-
Blood Tests: Assess hormonal levels crucial for ovulation and reproductive health.
-
Transvaginal Ultrasound: Evaluates ovarian follicles and uterine health, detecting structural abnormalities.
-
Laparoscopy: Invasive procedure to visualise pelvic organs, useful for diagnosing endometriosis or pelvic adhesions.
-
Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) Level: Indicates ovarian reserve, helping predict response to fertility treatments.
Diagnosis of Male Infertility
For men experiencing infertility, diagnostic steps include:
- Semen Analysis: Evaluates sperm count, morphology and motility to assess fertility potential.
- Blood Test: Identifies hormonal imbalances (e.g. testosterone) and genetic abnormalities affecting fertility.
- Scrotal Ultrasound: Detects varicoceles or structural defects in the testicles that impair sperm production.
Why Choose Us
Choosing the right fertility clinic is crucial for starting your family. At Birla Fertility & IVF, we offer personalised care with expert specialists guiding you every step of the way. Our advanced labs and outstanding success rates have helped over 2,30,000 patients achieve their dream of parenthood.
Frequently Asked Questions
IVF is often recommended for various fertility issues, using (ART) such as IVF, IUI, ICSI, blastocyst culture, and surgical interventions to fix structural abnormalities to achieve pregnancy
Fertility treatment begins with testing to diagnose the cause, followed by medications, surgery (if required), and ART procedures like IVF, IUI, ICSI, etc., based on patient’s unique requirements.
No. Studies have shown that using birth control does not affect fertility in future.
Track ovulation, maintain a healthy weight, avoid smoking/alcohol and consider preconception care to boost fertility and chances of conception.
Book an appointment
Hassle-Free Appointment Booking
Select Preferences
I know my doctor
Costs for Various Treatments in India
- Double Marker Test Cost in India
- Transvaginal Ultrasound Cost in India
- Hysterectomy Surgery Cost in India
- Testosterone Test Cost in India
- Adenomyosis Surgery Cost in India
- Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment Cost in India
- Miscarriage Treatment Cost in India
- Bartholin Cysts Treatment Cost in India
- Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT) Cost in India
- Endometrial Receptivity Analysis (ERA) Cost in India
- 3D Ultrasound with Color Doppler Cost in India
- Endometriosis Treatment Cost in India
- Embryo Freezing Cost in India
- Semen Analysis Test Cost in India
- Azoospermia Treatment Cost in India
- Egg Donor IVF Cost in India
- HyCoSy Test Cost in India
- Endometrial Biopsy Cost in India
- HSG Test Price in India
- NT NB Scan Cost in India
- FSH Test price in India
- E2 (Estradiol) Serum Test Cost in India
- Surrogacy Cost in India
- Sperm Freezing Cost in India
- Varicocele Cost in India
- Egg Freezing Cost in India
- IUI Treatment Cost in India
- IVF Cost in India
- AMH Test Cost in India
- ICSI Treatment Cost in India
- STD Test Cost in India
Specialist for Various Treatments in India
- Cervical Cancer Doctors in India
- Infertility Doctor in India
- ICSI Doctors in India
- Best Gynaecologists in India
- Uterine Fibroids Specialists in India
- Erectile Dysfunction Treatment Specialists in India
- Endometriosis Treatment Specialists in India
- Hormonal Specialists in India
- Endocrinologists in India
- Azoospermia Doctors in India
- PCOS Doctors in India
- Varicocele Doctors in India
- Best Doctors for Ovarian Cysts in India
- Male Infertility Specialists in India
- IVF Doctors in India
- IUI Doctors in India
- Hormone Specialists in India

 Our Centers
Our Centers