What is Altruistic Surrogacy – Process, Cost, Pros & Cons

Table of Contents
- What is Altruistic Surrogacy?
- Difference Between Altruistic and Commercial Surrogacy
- Who Can Choose Altruistic Surrogacy?
- Finding an Altruistic Surrogate in India
- Advantages of Altruistic Surrogacy
- Disadvantages of Altruistic Surrogacy
- The Process of Altruistic Surrogacy
- Cost of Altruistic Surrogacy
- Legalities Involved in Altruistic Surrogacy
Are you unable to conceive and wish to go for surrogacy as an alternative? Or, in case you can conceive, do you want to volunteer as a surrogate?
If the answer to either one of the questions is yes, keep reading. As discussed below are all the things you need to know about altruistic surrogacy, which you can opt for without being exploited.
What is Altruistic Surrogacy?
Just like other surrogacies, altruistic surrogacy involves a surrogate (close relative or friend) carrying a baby in her womb for a couple and giving birth to that baby. And once the baby has been born – handing over the baby to the couple.

Besides this, altruistic surrogacy is different from surrogacy like commercial surrogacy in other aspects.
In altruistic surrogacy as a couple, you don’t have to compensate the surrogate with a monetary fee. Instead, you only have to pay or reimburse the surrogate’s medication, medical-related expenses, and insurance coverage.
Difference Between Altruistic and Commercial Surrogacy
The primary difference between altruistic and commercial surrogacy lies in the financial compensation provided to the surrogate.
|
Aspect |
Altruistic Surrogacy |
Commercial Surrogacy |
|---|---|---|
|
Surrogate compensation |
No fee, only reimbursement of expenses |
The surrogate receives a fee in addition to expense reimbursement |
|
Motivation |
Helping others, empathy, family ties |
Financial gain, helping others |
|
Legal complexity |
Generally less complex because of the absence of financial agreements |
More complex because of financial contracts and compensation |
Who Can Choose Altruistic Surrogacy?
Repeated IVF Failures
Many couples struggle with infertility due to conditions like low ovarian reserve, age-related fertility decline, or repeated IVF failures. Altruistic surrogacy provides a viable option to have a biological child when natural conception isn’t possible.
Uterine Structural Issues
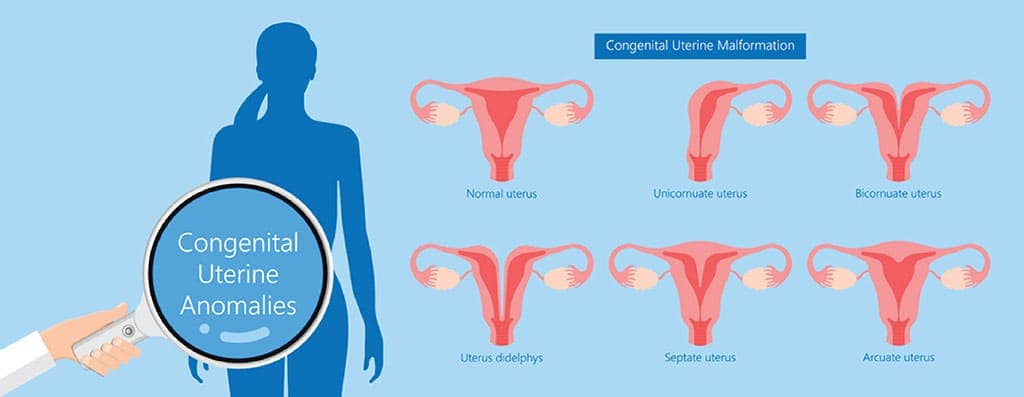
Genetic abnormalities such as a bicornuate or septate uterus, common causes of recurrent miscarriages in women, make carrying a pregnancy to term difficult. Surrogacy bypasses these complications.
Chronic Uterine Conditions
Untreatable conditions like severe endometriosis, fibroids, or adenomyosis can hinder conception. In India, where these conditions often go undiagnosed or are diagnosed late, surrogacy becomes a practical alternative for family building.
Health-Related Risks
Women with life-threatening conditions like cardiac disorders, severe diabetes, or cancer may be advised against carrying a pregnancy to protect both their health and the baby’s safety.
Complications from Previous Pregnancies
Past pregnancies complicated by issues like preeclampsia, uterine rupture, or postpartum haemorrhage may lead doctors to recommend surrogacy for subsequent family planning.
Hysterectomy
Women who have undergone hysterectomy due to conditions like uterine cancer or severe pelvic infections cannot conceive naturally, making surrogacy their primary route to parenthood.
Finding an Altruistic Surrogate in India
Finding an altruistic surrogate can be a delicate and emotionally rewarding process. In India, one of the most effective ways to find an altruistic surrogate is through personal networks. By reaching out to trusted friends, family, and acquaintances, you can find individuals willing to help, fostering emotional connections and ensuring shared values. This approach is especially relevant as altruistic surrogacy is the only legal form allowed under Indian law, which prohibits any payment beyond medical expenses and insurance coverage for the surrogate.
The Surrogacy (Regulation) Act, 2021, mandates that surrogates be close relatives, must have at least one child of their own, and must consent in writing after undergoing thorough medical and psychological assessments.
Advantages of Altruistic Surrogacy
Altruistic surrogacy offers several benefits for both the intended parents and the surrogate:
1. Stronger Emotional Connection
The altruistic nature of this arrangement promotes a deeper emotional connection between the intended parents and the surrogate, based on trust, empathy, and a shared desire to welcome a child into a loving family.
2. Affordability
Altruistic surrogacy is more affordable because surrogates are not paid beyond medical and pregnancy-related expenses, such as doctor visits, medications, and travel. This significantly reduces the overall cost compared to compensated surrogacy, where surrogates receive a fee for their services.
While intended parents still face costs for medical treatments (like IVF) , agency fees (for matching, legal support, and counselling), legal services (drafting contracts and ensuring parental rights), and insurance for the surrogate, the lack of compensation to the surrogate makes altruistic surrogacy a more cost-effective option. This structure makes surrogacy accessible to a broader range of intended parents.
3. Simplified Legal Process
The legal process for altruistic surrogacy in India is generally simpler compared to commercial surrogacy due to the absence of financial compensation beyond medical expenses. The Surrogacy (Regulation) Act, 2021, governs the entire process, focusing on eligibility criteria and the responsibilities of all involved parties.
Key aspects of this simplified legal process include:
-
Clear Agreements: Centred around medical expenses and the surrogate’s role, these contracts are simpler than those in commercial surrogacy. It has no complex cost structures, as the surrogate is not compensated beyond necessary medical costs.
-
Parental Rights and Surrogacy Contracts: Legal contracts ensure medical coverage and legal custody of the child are clarified. Once the child is born, this ensures that the intended parents are legally recognised as the parents after a court procedure.
-
Fewer Legal Conflicts: Without financial transactions, the risk of disputes over compensation is minimized. However, ensuring that all parties agree on the terms, especially regarding medical care and the child’s parentage, remains essential.
Disadvantages of Altruistic Surrogacy
While altruistic surrogacy has many advantages, it is essential to consider the potential drawbacks:
1. Strained Relationships:
The surrogacy process may put a strain on relationships, especially if the surrogate is a close friend or family member. Misunderstandings or unmet expectations may cause unforeseen expenses or complications occur.
2. Emotional Risks:
Surrogacy can have significant emotional impacts on the surrogate, including:
-
Mental Stress: Hormonal changes and the pressure of surrogacy may trigger anxiety and stress.
-
Attachment Issues: Emotional attachment to the baby may lead to difficulty after birth.
-
Postpartum Emotional Changes: Surrogates may experience postpartum depression or emotional shifts after delivery.
3. Physical Risks
The physical demands of surrogacy include:
-
Health Risks: IVF pregnancy is not immune to complications like gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, or high blood pressure.
-
Physical Strain: Nine months of pregnancy can cause fatigue, back pain, and swelling.
-
Labour and Delivery: The physical toll of labour can be intense, with potential recovery challenges.
-
Long-Term Impact: Multiple pregnancies can lead to lasting effects, such as pelvic floor damage or reproductive health issues.
Both emotional and physical risks need to be carefully managed for the surrogate’s well-being.
The Process of Altruistic Surrogacy
While the process of altruistic surrogacy is similar to that of commercial surrogacy, there are some key differences:
-
Finding a Surrogate: In altruistic surrogacy, the surrogate is usually someone the intended parents already know and trust, such as a close friend or family member.
-
Medical Preparations: Medical screenings include blood tests to check for infections and underlying health conditions, a physical examination, and a reproductive health evaluation, which may involve ultrasounds or hysteroscopies to assess the condition of the uterus.
Psychological evaluations are equally important. These screenings help determine the surrogate’s mental preparedness for the emotional demands of surrogacy, and counselling is provided for both her and her family to address concerns. In addition, the surrogate will undergo infectious disease testing to safeguard the health of both herself and the baby.
-
Legal Preparations: Once the medical screenings are complete, legal preparations follow. A contract is drawn up to clarify the roles and rights of both the surrogate and the intended parents. Even in altruistic surrogacy, the intended parents cover all pregnancy-related expenses, including medical care. The contract also protects the parental rights of the intended parents and outlines the surrogate’s responsibilities during the pregnancy.
-
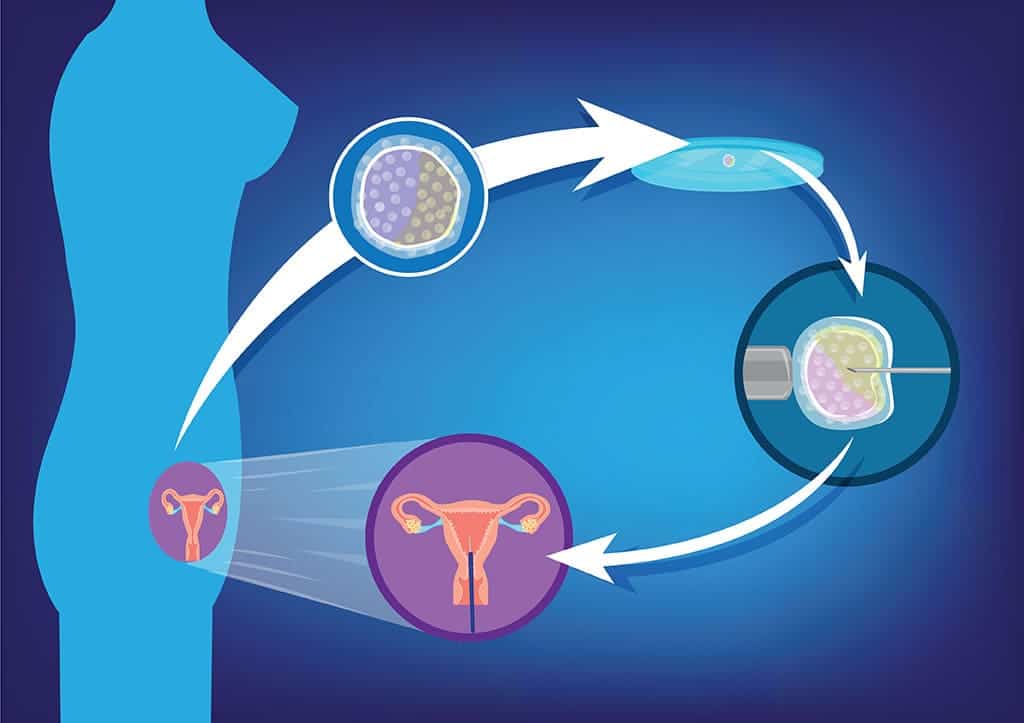
Embryo Transfer: The next step is the embryo transfer process, which begins with the creation of the embryo through IVF. Eggs from the intended mother (or an egg donor) are fertilised with sperm in a lab, and once the embryos are viable, they are carefully transferred into the surrogate’s uterus. To prepare for this, the surrogate undergoes hormone treatments to prime her uterus for the embryo to implant successfully. The transfer itself is a quick, relatively simple procedure, and after 10 to 14 days, a pregnancy test is conducted to confirm the result.
-
Pregnancy and Birth: Throughout the pregnancy, the surrogate will have regular check-ups to monitor her and the baby’s health. The intended parents often stay closely involved during these visits, supporting the surrogate and attending key appointments.
Cost of Altruistic Surrogacy
Although altruistic surrogacy excludes surrogate compensation, there are still significant costs involved. Here’s a concise breakdown:
-
Medical Expenses
-
Fertility Treatments: IVF, ICSI, or embryo transfer (₹3–₹6 lakhs).
-
Pregnancy Monitoring: Regular ultrasounds (transvaginal, abdominal) and blood tests.
-
Medications: Fertility drugs, hormone supplements, and general pregnancy care.
-
-
Legal & Insurance Costs
-
Drafting surrogacy agreements and custody formalities (₹2–₹5 lakhs).
-
Insurance for surrogate’s postpartum complications for 16 months.
-
-
Counselling Services
-
Emotional support for surrogate and intended parents during and after the process.
-
-
Miscellaneous Expenses
-
Maternity needs, travel, and routine check-ups (₹1–₹2 lakhs).
-
Legalities Involved in Altruistic Surrogacy
The legal aspects of altruistic surrogacy are crucial to ensure a smooth and protected journey for all parties involved.
-
Gestational Surrogacy Agreement (GSA)
-
A legally binding contract outlining the roles, responsibilities, and risks for all parties, ensuring clarity and protection.
-
-
Legal Framework
-
Governed by the Surrogacy (Regulation) Act, 2021, which permits altruistic surrogacy for eligible married heterosexual couples.
-
Surrogate must be a close relative, married, and a mother of at least one child.
-
-
Documents Required
-
For Intended Parents: Medical board certification of infertility, marriage certificate, and age proof (women: 23–50; men: 26–55).
-
For Surrogate: Proof of relationship, health clearance, and consent forms.
-
-
Process and Timeline
-
Medical and legal evaluations: 2–4 months.
-
Court approvals and documentation: 1–2 months.
-
-
Management of Legalities
-
Handled by fertility centres or lawyers to ensure compliance with laws and smooth execution.
-
By addressing these legalities, altruistic surrogacy can proceed with clarity and mutual respect, prioritising the well-being and interests of both the surrogate and the intended parents.
Altruistic surrogacy is the only form of surrogacy allowed in India. Under The Surrogacy (Regulation) Act 2021, surrogates are not paid beyond essential medical costs. This ensures that the focus remains on helping families grow, rather than monetary gain. The law safeguards against exploitation and upholds ethical practices. Ministry of Law and Justice. (2021).
A Word from the Expert
“Altruistic surrogacy is a beautiful example of human compassion and selflessness. It takes a special kind of person to carry a child for someone else, motivated solely by the desire to help them experience the joy of parenthood. While the process can be emotionally and physically challenging, the reward of seeing the intended parents hold their baby for the first time is truly priceless.”~ Dr. K U Kunjimoideen
Our Fertility Specialists
Related Blogs
To know more
Birla Fertility & IVF aims at transforming the future of fertility globally, through outstanding clinical outcomes, research, innovation and compassionate care.
Had an IVF Failure?
Talk to our fertility experts

 Our Centers
Our Centers