How Does Prostatitis Affect Male Fertility?

Table of Contents
Prostatitis can cause discomfort, anxiety, and even confusion, particularly if you’re concerned about how it might impact your ability to have children.
Many men quietly question whether symptoms like pain, irritation, or frequent urination could reduce their chances of becoming pregnant or have an impact on their fertility. You’re not alone if you’re feeling anxious or overworked.
In actuality, prostatitis is widespread and, with the correct medical attention, is usually curable. It can be far less scary if you know how it impacts sperm health, sexual function, and general reproductive health. Together, let’s navigate it so you feel more knowledgeable, encouraged, and optimistic about your reproductive path.
What is Prostatitis?
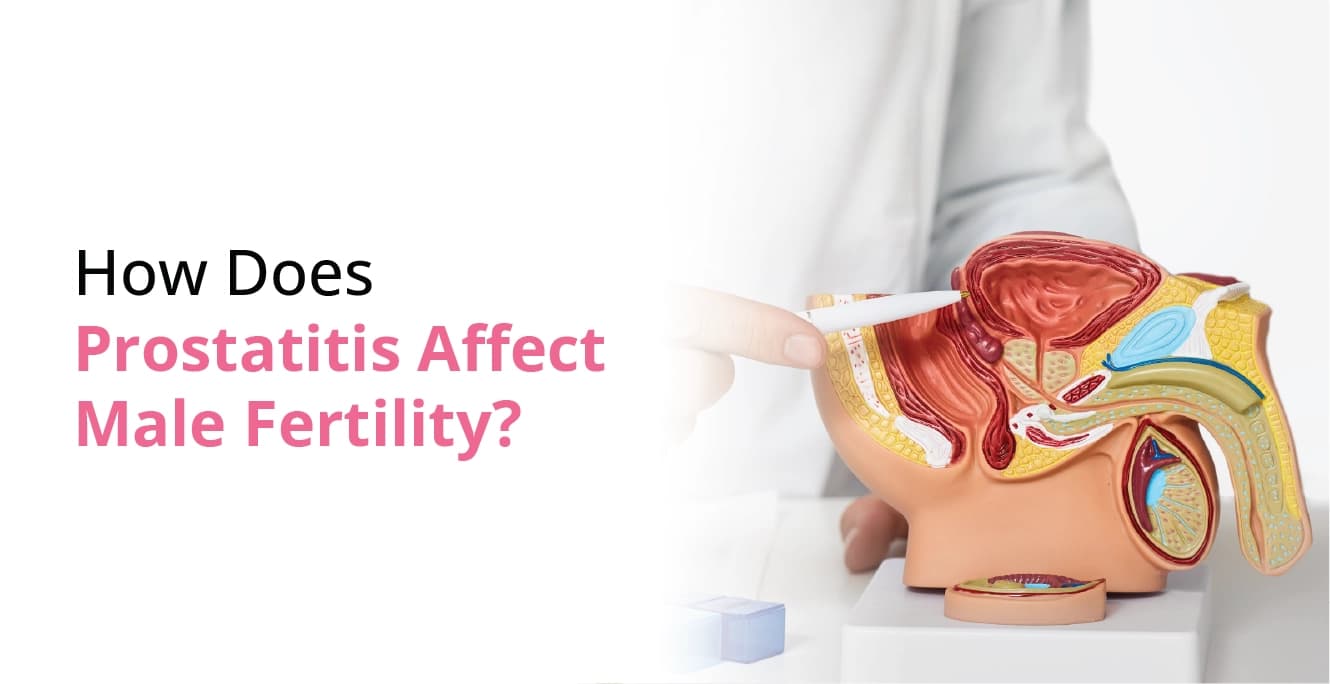
Understanding the function of the prostate in the reproductive system is crucial to comprehending how an enlarged prostate may impact fertility. Seminal fluid is produced by the prostate, a walnut-sized gland. During an orgasm, this fluid combines with sperm generated in the testicles to create semen, which is expelled.
The prostate is essential for male fertility because seminal fluid nourishes and shields sperm. Although the prostate doesn’t directly create sperm, the quality of semen and the ejaculation process can be greatly impacted by its health.
Role of the Prostate in Reproductive Health
The prostate is a chestnut-sized gland that weighs roughly 30 grams. It is found inside the body and is a component of the male reproductive system. The production of a fluid that, when combined with sperm cells from the testicles and fluids from other glands, forms semen is the primary function of the prostate. During ejaculation, the prostate’s muscles also make sure that the semen is pushed firmly into the urethra and subsequently released forth.
A healthy prostate supports the perfect sperm habitat and migration. However, when the prostate is inflamed, sperm motility may be hindered, semen composition may alter, or ejaculation may be totally disturbed.
Causes of Prostatitis
There are a lot of reasons behind prostatitis, and understanding them can help you figure out the underlying causes:
- Bacterial infection- When bacteria from the urinary tract enter the prostate gland, they can result in prostatitis. This may happen after a urinary tract infection, unprotected sex, or even due to poor hygiene.
- Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome – It may be linked to pelvic floor muscle tension, stress, nerve inflammation, autoimmune reactions, or prolonged sitting.
- Injury- This is one of the most common causes of prostatitis. Catheter use, prostate stones, dehydration, hormonal imbalances, or a weakened immune system can also cause prostatitis.
Sometimes, no exact cause is identified, which can be frustrating, but effective treatments are still available even for non-bacterial cases.
Types of Prostatitis
There are multiple types of prostatitis, each with unique causes and treatments:
- Acute Bacterial Prostatitis – It is a serious bacterial infection that results in fever, chills, and excruciating pain. These develop rapidly and need immediate medical attention.
- Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis – It is a type of prostatitis that is persistent and occurs due to recurrent bacterial infections. Though they might appear and disappear over several months, their symptoms can be less severe than those of Acute bacterial prostatitis.
- Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome (CPPS)- It is the most common type of prostatitis, which manifests as persistent pain, discomfort, and urine issues. Inflammation, tense muscles, or nerve problems are common causes.
- Asymptomatic Inflammatory Prostatitis- Prostate inflammation without any apparent symptoms is known as asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis. Tests for other reproductive or urinary issues typically reveal it.
Symptoms of Prostatitis
Depending on the type, symptoms can vary, but the most common ones are:
- Lower back, lower abdominal, or pelvic pain
- Penile, testicular, or perineal pain
- Burning or painful urine
- Urgent or frequent need to urinate
- Poor urine flow or difficulty initiating
- Ejaculation that hurts
- Blood in semen or pee (in some situations)
- Fever or chills (mostly in acute prostatitis)
Diagnosis of Prostatitis
Diagnosing prostatitis involves a combination of assessments:
- Review of medical history and symptoms to determine severity and trend
- Physical examination to assess prostate tenderness, including a digital rectal exam (DRE)
- Tests for infection or inflammation in the urine
- Tests for infection indicators in the blood
- Analysing semen to determine fertility and identify inflammation
- Culture of prostate fluid (in certain situations)
- If structural problems or stones are detected, use an MRI or ultrasound.
These tests help differentiate between bacterial and non-bacterial prostatitis, guiding effective treatment.
Treatment Options For Prostatitis
Medications
- Alpha-blockers: They facilitate urination by relaxing the muscles surrounding the urethra.
- 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors: By reducing hormone levels that promote prostate growth, these drugs aid in prostate shrinkage.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics may be recommended if prostatitis or an infection are present.
- Urinary symptoms may be lessened by these treatments, however ejaculation may also be impacted. For instance, retrograde ejaculation, which can lower semen volume and impact fertility, is known to be brought on by certain alpha-blockers.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
Minimally invasive treatments including laser therapy or transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) may be suggested for men with more severe cases of prostatitis. In order to ease urinary blockage, these treatments eliminate or remove extra prostate tissue.
These treatments can alleviate urinary problems, but they may have adverse effects that compromise fertility. For instance, one common side effect of TURP is retrograde ejaculation.
Lifestyle Changes
Some men can modify their lifestyles to handle symptoms. Some of these tips are:
- Cutting back on fluids before bed to reduce nocturia
- Steer clear of alcohol and coffee as these can irritate the bladder.
- Strengthening the muscles used for urine and ejaculation with pelvic floor exercises
- By improving sexual and urinary health, these modifications can lessen the negative effects of BPH on fertility.
How Does Prostatitis Affect Male Fertility?
Whether a low sperm count is directly caused by an enlarged prostate is one of the main questions. We must comprehend how thay affects the male reproductive system in order to respond to this. Although prostatitis doesn’t directly lower sperm count, it can have a number of indirect effects on male fertility and sperm quality:
Ejaculatory Issues
Ejaculation problems are one of the consequences of an enlarged prostate. Reduced semen volume, painful or delayed ejaculation, or even retrograde ejaculation in which semen enters the bladder rather than leaving the body are all possible symptoms for men with prostatitis. Fertility may be impacted by several circumstances, which can reduce the quantity of sperm that enters the vagina.
Although the testicles are the primary site of sperm production, problems with ejaculation can lessen the sperm’s ability to fertilise an egg. For instance, decreased semen volume might dilute sperm concentration, resulting in a lower ejaculate sperm count.
Inflammation and Infection
Men who have an enlarged prostate may be more vulnerable to urinary tract infections (UTIs) or prostatitis, an inflammation of the prostate. Seminal fluid production can be hampered by prostatitis, whether it is bacterial or not. Sperm motility and viability can be decreased by inflammation, which can change the quality of the fluid that feeds sperm.
Furthermore, persistent inflammation in the reproductive system or prostate may damage sperm DNA, resulting in lower-quality sperm.
Blockage of Seminal Pathways
The tube that both urine and semen go through is called the urethra, and it is surrounded by the prostate. The urethra may become compressed or blocked when the prostate grows. This compression may make it more difficult to release seminal fluid and sperm during ejaculation, which could lower the number of sperm that enter the female reproductive system.
A obstruction in the seminal pathways can prevent healthy sperm from being transported and delivered, which lowers the chance of conception even if the testicles generate them.
Impact of Prostate Cancer Treatments on Fertility
In some cases, men may experience both benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH) and prostate cancer, and the treatments for prostate cancer can further affect male fertility. Prostate cancer treatments, such as radiation therapy, hormone therapy, or surgery, can affect sperm production and quality. For example, hormone therapy used to reduce prostate size or cancer growth can suppress testosterone levels, which may reduce sperm production and lower fertility. Similarly, surgical removal of the prostate, known as a prostatectomy, can result in issues like erectile dysfunction or the inability to ejaculate, directly impacting a man’s ability to father children.
Conclusion
Prostatitis can feel overwhelming, especially when you’re concerned about how it may affect your fertility or overall well-being. But with the right information and timely medical care, most men recover fully and regain normal reproductive function. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and impact on sperm health can empower you to recognize early warning signs and seek help before the condition becomes chronic.
Whether your symptoms are mild or persistent, remember that prostatitis is treatable, and many men go on to conceive naturally after addressing the inflammation or infection. Take small steps toward prevention, listen to your body, and don’t hesitate to consult a specialist. Supporting your prostate health today can play a big role in protecting your fertility tomorrow.
FAQ’s
What are the natural ways of preventing prostatitis?
Staying hydrated, maintaining good hygiene, practising safe sex, avoiding long sitting hours, and regular ejaculation can help reduce the risk.
Can it be treated permanently?
Yes, acute cases usually resolve fully, but chronic prostatitis may recur and often needs long-term management.
Does it cause low sperm count?
Not usually, but severe or chronic infections can temporarily affect sperm quality.
Our Fertility Specialists
Related Blogs
To know more
Birla Fertility & IVF aims at transforming the future of fertility globally, through outstanding clinical outcomes, research, innovation and compassionate care.
Had an IVF Failure?
Talk to our fertility experts

 Our Centers
Our Centers